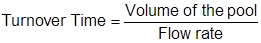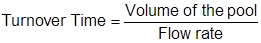
Relevant terms are defined in Reference Joint Appendix JA1.
The following are terms that are either not defined in JA1 or expansions to the Appendix I definitions.
Energy Factor (EF) of a water heater is a measure of overall water heater efficiency for most residential water heaters, as determined using the applicable test method in the Appliance Efficiency Regulations. Typical gas storage water heaters have typical EFs of about 0.60-0.70, electric storage water heaters approximately 0.90, and gas instantaneous units approximately 0.80-0.94.
External tank insulation can be applied to the exterior of storage type water heater tanks. When installed, water heater insulation should be applied to completely cover the exterior of the water heater, but should not conceal controls or access ports to burners, obstruct combustion air openings, or interfere in any way with safe water heater operation. Insulation of top and bottom surfaces is not necessary.
Recovery energy is the energy used to heat water.
Recovery load is the load on the water heater due to hot water end uses and distribution losses.
Thermal efficiency is defined in the Appliance Efficiency Regulations as a measure of the percentage of heat from the combustion of gas or oil that is transferred to the hot water as determined using the applicable test methods.
Flow Rate is the volume of water flowing through the filtration system in a given time, usually measured in gallons per minute.
Nameplate Power is the motor horsepower (hp) listed on the nameplate and the horsepower by which a pump is typically sold.
Pool Pumps usually come with a leaf strainer before the impeller. The pumps contain an impeller to accelerate the water through the housing. The motors for residential us pumps are included in the pump purchase but can be replaced separately. The pumps increase the “head” and “flow” of the water. Head is necessary to move fluid through pipes, drains, and inlets, push water through filters and heaters, and project it through fountains and jets. Flow is the movement of the water used to maintain efficient filtering, heating, and sanitation for the pool.
Return refers to the water in the filtration system returning to the pool. The return lines or return side, relative to the pump, can also be defined as the pressure lines or the pressure side of the pump. Water in the returns is delivered back to the pool at the pool inlets.
Service Factor. The service factor rating indicates the percent above nameplate horsepower at which a pump motor may operate continuously when full rated voltage is applied and ambient temperature does not exceed the motor rating. Full-rated pool motor service factors can be as high as 1.65. A 1.5 hp pump with a 1.65 service factor produces 2.475 hp (total hp) at the maximum service factor point.
Suction created by the pump is how the pool water gets from the skimmers and drains to the filtration system. The suction side and suction lines refer to the vacuum side of the pump. It is at negative atmospheric pressure relative to the pool surface.
Total Dynamic Head (TDH) refers to the sum of all the friction losses and pressure drops in the filtration system from the pools drains and skimmers to the returns. It is a measure of the system’s total pressure drop and is given in units of either psi or feet of water column (sometimes referred to as “feet” or “feet of head”).
Total Motor Power or T-hp, refers to the product of the nameplate power and the service factor of a motor used on a pool pump.
Turnover is the act of filtering one volume of the pool.
Turnover Time (also called Turnover Rate) is the time required to circulate the entire volume of water in the pool or spa through the filter. For example, a turnover time of 6-hours means an entire volume of water equal to that of the pool will be passed through a filter system in six hours.