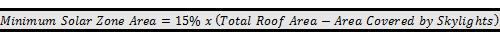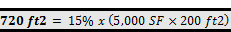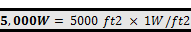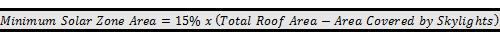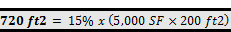9.5
Exceptions
There are five exceptions to the solar zone area requirement
described in §110.10(b)1B
Four of these five exceptions are described below. Although the language in
the Energy Standards implies that these four exceptions only apply to the solar
zone requirements, the intent of the Energy Standard is for the exceptions to
apply to the solar zone requirement as well as the interconnection pathway
requirements described in §110.10(c)
and the documentation requirements described in §110.10(d)
•
PV System is Permanently Installed (Exception 1 to
§110.10(b)1B): Buildings are exempt from solar zone, interconnection
pathway and documentation requirements if a solar PV system with a nameplate
direct current (DC) power rating of no less than 1 watt per ft2 roof area is permanently
installed at the time of construction. The nameplate rating must be measured
under Standard Test Conditions. The permanently installed solar PV system can be
installed anywhere on the building site. To verify compliance with this exception form
NRCI-SPV-01-E Certificate of Installation: Solar Photovoltaic System must
be submitted.
•
SWH System is Permanently Installed (Exception 2 to
§110.10(b)1B): Buildings are exempt from solar zone, interconnection
pathway and documentation requirements if a domestic SWH system is permanently
installed at the time of construction. The SWH system must comply with §150.1(c)8Ciii,
the prescriptive solar water heating system requirements when installing a
water-heating system serving multiple dwelling units. The permanently
installed domestic SWH collectors can be installed anywhere on the building
site. To verify compliance with this exception form NRCI-STH-01-E Certificate
of Installation: Solar Water Heating System must be submitted.
•
High-rise Multifamily Building with Occupant Controlled Smart
Thermostats (OCST) and High-efficacy lighting (Exception 4 to
§110.10(b)1B): High-rise multifamily buildings that comply with items
1 through 5 below are exempt from solar zone, interconnection pathway and
documentation requirements.
1.
All thermostats in each dwelling unit are Occupant Controlled Smart Thermostats (OCST)
with communications capabilities enabled to receive and respond to Demand
Response signals. An OCST is a setback thermostat with communication
capabilities that enable the occupant to receive Demand Response related
messages and respond to those signals by automatic adjustment of the
thermostat setpoint as described in Joint Appendix
JA5 (subject to occupant participation). Enabling communications
capabilities requires that the OCST has one of the following: onboard
communications capabilities, an installed communications module for OCSTs with
removable communications module(s), or an installed communications gateway for
an OCST where an external gateway is required for communications.
OCST must be certified by
the Energy
Commission to meet the requirements described in Joint Appendix JA5.
2.
All permanently installed indoor lighting in each dwelling unit is high efficacy
and is installed in kitchens, bathrooms, utility rooms, and private garages at a
minimum. Permanently installed nightlights complying with §150.0(k)1E
and lighting integral to exhaust fans complying with §150.0(k)1F are
allowed.
3.
All permanently installed lighting in bathrooms is controlled by a
vacancy
sensor, except for one high efficacy luminaire with total lamp wattage no
greater than 26 watts.
4.
Every room that does not have permanently installed lighting has at least one
switched receptacle installed.
5.
All permanently installed outdoor lighting for private patios, entrances, balconies, and
porches is high efficacy and controlled by an on/off switch and either a
photocontrol or astronomical time clock or energy management
control system.
•
Roof Designed for Vehicle Traffic or Parking or Heliport (Exception 5
to section 110.10(b)1B):
•
Buildings are exempt from solar zone interconnection pathway and
documentation requirements if the roof is designed for vehicle traffic (parking lot) or if
the roof is designed as a helicopter landing zone.
Exception (Exception 3 to §110.10(b)1B
allows the minimum solar zone are to be reduced if the solar access at the
building site is limited. Exception 3 to §110.10(b)1B is described in more
detail above in the minimum solar zone area section of this chapter (Section
9.3.1).
Example
9-5
Question
An office building has a total roof area of 5,000 ft2.
The total roof area covered by skylights is 200 ft2. A solar PV
system with a DC power rating (measured under Standard Test Conditions) of 4 kW
will be installed. The collection panels for the 4 kW system will cover 400
ft2. Does the building have to have to include a solar zone 'in 'addition
to the installed solar PV system?
Answer
Yes. To be exempt from the solar zone requirement, the
solar PV system must have a power rating equal to 1 watt for every square foot
of roof area, or in this case 5kW (see equation below).

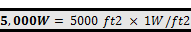
The minimum solar zone for this building is 720
ft2 (see calculation below). The 400 ft2 on which the
solar PV system is installed does count towards the minimum solar zone area, so
an additional 320 ft2 would need to be allocated to complete the
minimum solar zone requirement.