
Luminaires and light sources emit light and provide illumination to spaces. The Energy Standards include a system of classification to account for the power of luminaires and lighting systems and to use the information for compliance purpose.
Below is the list of various types of luminaires as described and classified in Section 130.0(c) of the Energy Standards:
•Luminaires with line-voltage lamp holders
•Luminaires with ballasts
•Inseparable solid state lighting (SSL) luminaires and SSL luminaires with remote ballasts
•LED tape lighting and LED linear lighting
•Modular lighting systems
•Other lighting equipment
For meeting the prescriptive or performance requirements for indoor lighting, the wattage of all planned lighting systems, including permanent lighting and portable lighting, shall be determined as follows.
A. Luminaires with line-voltage lamp holders
The wattage of luminaires with line-voltage lamp holders not containing permanently installed ballast or transformers shall be the maximum rated wattage of the luminaire.
For recessed luminaires with line-voltage medium base sockets, wattage shall not be less than 50 watts per socket, or the rated wattage of the installed JA8 compliant lamps.
The 2019 Energy Standards allow the wattage of JA8 lamps to be used as the wattage of recessed luminaires. This provides another option for designers, engineers and installers for their compliance use of luminaires with line-voltage lamp holders.
Figure 5-2 Sample of Luminaire with line-voltage lamp holders

Source: CEC Staff
B. Luminaires with ballasts
The wattage of luminaires with permanently installed or remotely installed ballasts shall be the operating input wattage of the rated lamp/ballast combination.
This wattage information can be found in the ballast manufacturer’s catalogs based on independent testing lab report as specified in UL 1598.
Figure 5-3 Samples of Luminaires with ballasts:
Fluorescent-lamp luminaire (Left); HID-lamp luminaire (Right)

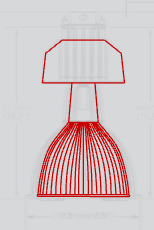
Source: Acuity Brands Lighting, Inc.; Source: CEC Staff
C. Inseparable Solid State Lighting (SSL) luminaires and SSL luminaires with remotely mounted drivers
The wattage of inseparable SSL luminaires and SSL luminaires with remote ballasts shall be the maximum rated input wattage of the SSL luminaires.
Inseparable SSL luminaires are luminaires manufactured with the solid state lighting components which are not readily removed or replaced from the luminaires by the end users.
SSL luminaires shall be tested in accordance with UL 1598, 2108, 8750 or IES LM-79.
Figure 5-4 Samples of SSL Luminaires:
Recessed Downlight Luminaires (Left; Right)


Source: © 2018 Lutron Electronics Co., Inc. All rights Reserved
D. LED tape lighting and LED linear lighting
LED tape lighting can be installed in length by installers on a project site as determined by the lighting design requirements. LED tape lighting is not like legacy luminaires which are manufactured in a pre-determined dimension per customer order.
The wattage of the luminaire or lighting system shall be the sum of the installed length of the tape lighting times its rated linear power density in W/ft (or the maximum rated input wattage of the driver or power supply providing power to the lighting system).
Tape lighting shall be tested in accordance with UL 2108, 8750, or IES LM-79.
Figure 5-5 Samples of Tape Lighting


Source: NORA Lighting
E. Modular lighting systems
Track mounted luminaires as well as rail mounted luminaires are examples of modular lighting systems. The wattage of modular lighting systems that allow the addition or relocation of luminaires without altering the wiring of the systems shall be determined as follows.
The wattage shall be the greater of 30 watts per linear foot of track or plug-in busway; or, the rated wattage of all of the luminaires in the system (where the luminaire wattage is as specified by UL 1574, 1598, 2108, or 8750)
1. For line-voltage track lighting and plug-in busway served by a track lighting current limiter, the wattage shall be the volt-ampere rating of current limiter as specified by UL 1077
2. For line-voltage track lighting and plug-in busway served by a track lighting protection panel, the wattage shall be the sum of ampere rating of all of the overcurrent protection devices times the branch circuit voltage for the track lighting protection panel; or
3. For other modular systems with power supplied by a driver, power supply or transformer, including low-voltage lighting systems, the wattage shall be the maximum rated input wattage of the driver, power supply or transformer as specified by UL 2108 or 8750
4. For power-over-Ethernet lighting system, the wattage shall be the total power rating of the system less any installed non-lighting devices.
Figure 5-6 Samples of Modular Lighting Systems:
A Track Lighting System 3D View (Top);
Track Lighting Systems in a Lobby Lighting Application (Bottom)
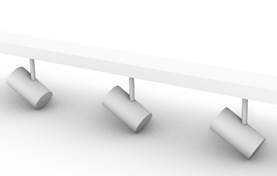
Source: CEC

Source: Acuity Brands Lighting, Inc.
F. Other lighting equipment
For all other lighting equipment not addressed by item A through E, the wattage of the lighting equipment shall be the maximum rated wattage of the lighting equipment, or operating input wattage of the system, based on independent testing lab reports as specified by UL1547, 1598, 2108, 8750, or IES LM-79.
Example 5-1 Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) Lighting
Question
What is a Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) lighting system?
Answers
A Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) lighting system is an emerging lighting technology which provides low-voltage direct current (DC) and communication over ethernet cabling. The direct current powers the luminaires of the system. Most conventional lighting systems use alternating current (AC) to power luminaires.
A PoE lighting system usually contains three main components – a powered device (PD), ethernet cabling, and power sourcing equipment (PSE) such as ethernet switches. PSE is a general term used for PoE power supply.
PSEs supply power via Ethernet cabling to PD’s, such as PoE luminaires.
Example 5-2 Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) Lighting
Question
What is the wattage of a PoE lighting system that contains a PoE switch, PoE luminaires, occupancy sensors, one daylight sensors, wall switch stations?
Answers
One way to determine the answer is to account for the wattage of all of the luminaires in the lighting system as the wattage of the PoE lighting system. Since there are nine PoE luminaires plus other non-lighting loads (sensors and switches), the wattage of the PoE lighting system is the sum of the wattage of all PoE luminaires excluding the sensors and switches.
Another way is to account for the total power rating of the system less any non-lighting devices such as occupancy sensors, sensing devices and switch controls.