

The piping for all space-conditioning and service water-heating systems with fluid temperatures 'listed in TABLE 120.3-A shall have the amount of insulation specified in Subsection (a) or (b). Insulation conductivity shall be determined in accordance with ASTM C335 at the mean temperature 'listed in TABLE 120.3-A, and shall be rounded to the nearest 1/100 Btu-inch per hour per square foot per °F.
Insulation shall be protected from damage, including that due to sunlight, moisture, equipment maintenance, and wind, including but not limited to, the following:
Insulation exposed to weather shall be suitable for outdoor service by either being rated by the manufacturer for outdoor use or by being covered e.g., protected by aluminum, sheet metal, painted canvas, or plastic cover. Cellular foam insulation shall be protected as above or painted with a coating that is water retardant and provides shielding from solar radiation that can cause degradation of the material.
Insulation covering chilled water piping and refrigerant suction piping located outside the conditioned space shall include a vapor retardant located outside the insulation (unless the insulation is inherently vapor retardant), all penetrations and joints of which shall be sealed.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 120.3: Factory-installed piping within space-conditioning equipment certified under Section 111 or 112.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 120.3: Piping that conveys fluids with a design operating temperature range between 60°F and 105°F.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 120.3: Gas piping, cold domestic water piping, condensate drains, roof drains, vents, or waste piping.
EXCEPTION 4 to Section 120.3: Where the heat gain or heat loss to or from piping without insulation will not increase building source energy use.
EXCEPTION 5 to Section 120.3: Piping that penetrates framing members shall not be required to have pipe insulation for the distance of the framing penetration. Metal piping that penetrates metal framing shall use grommets, plugs, wrapping or other insulating material to assure that no contact is made with the metal framing.
(a) For insulation with a conductivity in the range shown in TABLE 120.3-A for the applicable fluid temperature range, the insulation shall have the applicable thickness shown in TABLE 120.3-A.
(b) For insulation with a conductivity outside the range shown in TABLE 120.3-A for the applicable fluid temperature range, the insulation shall have a minimum thickness as calculated with:
INSULATION THICKNESS EQUATION
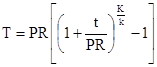
WHERE:
|
T |
= |
Minimum insulation thickness for material with conductivity K, inches. |
|
PR |
= |
Pipe actual outside radius, inches. |
|
t |
= |
Insulation thickness from TABLE 120.3-A, inches. |
|
K |
= |
Conductivity of alternate material at the mean rating temperature indicated in TABLE 120.3-A for the applicable fluid temperature range, in Btu-inch per hour per square foot per °F. |
|
k |
= |
The lower value of the conductivity range 'listed’ in Table 120.3-A for the applicable fluid temperature range, Btu-inch per hour per square foot per °F.
|

|
FLUID TEMPERATURE
RANGE |
CONDUCTIVITY
RANGE |
INSULATION MEAN RATING TEMPERATURE (°F) |
NOMINAL PIPE DIAMETER (in inches) | ||||
|
< 1 |
1 to <1.5 |
1.5 to |
4 to < 8 |
8 and larger | |||
|
INSULATION THICKNESS REQUIRED (in inches) | |||||||
|
Space heating, Hot Water systems (steam, steam condensate and hot water) and Service Water Heating Systems | |||||||
|
Above 350 |
0.32-0.34 |
250 |
4.5 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
5.0 |
|
251-350 |
0.29-0.31 |
200 |
3.0 |
4.0 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
4.5 |
|
201-250 |
0.27-0.30 |
150 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
2.5 |
3.0 |
3.0 |
|
141-200 |
0.25-0.29 |
125 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
2.0 |
|
105-140 |
0.22-0.28 |
100 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
|
| |||||||
|
Space cooling systems (chilled water, refrigerant and brine) | |||||||
|
40-60 |
0.21-0.27 |
75 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
Below 40 |
0.20-0.26 |
50 |
1.0 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1.5 |