The Standards apply to both nonresidential and residential buildings. This 'manual addresses the requirements for nonresidential buildings, including hotels, motels, and high-rise residential buildings (those over three stories above grade in height). The Residential Manual addresses the requirements for low-rise residential buildings, which include the single family and duplex residential buildings.
The Nonresidential Standards apply to all buildings of the California Building Code (CBC) occupancies of Group A, B, E, F, H, M, R, S or U. If these buildings are directly or indirectly conditioned, they must meet all mechanical, envelope, indoor, and outdoor lighting requirements of the Standards. Those buildings that are not directly or indirectly conditioned must only meet the indoor and outdoor lighting requirements of the Standards.
The Standards do not apply to CBC Group I or L. This group includes such buildings as hospitals, daycare, nursing homes, and prisons. The Standards also do not apply to buildings that fall outside the jurisdiction of California Building Codes, such as mobile structures. If outdoor lighting is associated with a Group I or L occupancy, it is exempt from the Standards requirement; however, if the outdoor lighting is part of any of occupancy groups 'listed above, it must comply with the Standards requirements.
Exception 1 to §100.0(a) states that qualified historic buildings, as regulated by the California Historical Building Code Title 24, Part 8 or California Building Code, Title 24, Part 2, Volume I, Chapter 34, Division II are not covered by the Standards. §140.6(a)3Q and Exception 13 to §140.7(a) clarify that indoor and outdoor lighting systems in qualified historic buildings are exempt from the lighting power allowances only if they consist solely of historic lighting components or replicas of historic lighting components. If lighting systems in qualified historic buildings contain some historic lighting components or replicas of historic components, combined with other lighting components, only those historic or historic replica components are exempt. All other lighting systems in qualified historic buildings must comply with the Standards.
The California Historical Building Code (CHBC) Section 102.1.1 specifies that all non-historical additions must comply with the regular code for new construction, including the Standards. CHBC Section 901.5 specifies that when new or replacement mechanical, plumbing, and/or electrical (including lighting) equipment or appliances are added to historic buildings; they should comply with the Standards, including the Appliance Efficiency Regulations.
The California State Historical Building Safety Board has final authority in interpreting the requirements of the CHBC and determining to what extent the requirements of the Standards apply to new and replacement equipment and other alterations to qualified historic buildings. It should be noted that in enacting the State Historical Building Code legislation, one of the intents of the Legislature was to encourage energy conservation in alterations to historic buildings (Health and Safety Code Section 18951).
Additional information about the CHBC can be found on the following website:
http://www.dgs.ca.gov/dsa/AboutUs/shbsb.aspx
Contact the State Historical Building Safety Board at (916) 445-7627.
The Residential Standards cover single-family and low-rise residential buildings (occupancy groups R1, R2, and R3) and CBC Group U buildings including:
1. All single-family dwellings of any number of stories
2. All duplex (two-dwelling) buildings of any number of stories
3. All multi-family buildings with three or fewer habitable stories above grade (Groups R 1 and R-2)
4. Additions and alterations to all the above buildings
5. Private garages, carports, sheds and agricultural buildings
|
Nonresidential Standards |
Residential Standards |
|
These Standards cover all nonresidential occupancies (Group A, B, E, F, H, M, R, S or U), as well as high-rise residential (Groups R-1 and R-2 with four or more habitable stories), and all hotel and motel occupancies. |
These Standards cover all low-rise residential occupancies including: |
|
Offices Retail and wholesale stores Grocery stores Restaurants Assembly and conference areas Industrial work buildings Commercial or industrial storage Schools and churches Theaters Hotels and motels Apartment and multi-family buildings, and long-term care facilities (Group R-2), with four or more habitable stories |
All single family
dwellings of any number of stories All duplex (two-dwelling) buildings of any number of stories (Group R-3) All multi-family buildings with three or fewer habitable stories above grade (Groups R-1 and R-2) Additions and alterations to all of the above buildings
|
|
Note: The Standards define a habitable story as one that contains space in which humans may live or work in reasonable comfort, and that has at least 50% of its volume above grade. | |
The Standards apply to any new construction that requires a building permit, whether for an entire building, for outdoor lighting systems, for signs, or for a modernization. The primary enforcement mechanism is through the building permitting process. Until the enforcement agency is satisfied that the building, outdoor lighting, or sign complies with all applicable code requirements, including the Standards, it may withhold the building permit (or, after construction, the occupancy permit).
The Standards apply only to the construction that is the subject of the building permit application (with the exception of existing spaces that are "conditioned" for the first time, in which case existing envelope components, and existing lighting systems, whether altered or not, must also show compliance with the Standards).
Other than for lighting, the Standards apply only to buildings that are directly or indirectly conditioned by mechanical heating or mechanical cooling. Section 1.7.17 provides detailed definitions of these terms.
Known Occupancy
Speculative buildings of known occupancy are commonly built by developers. For example, if a big box retail center or an office building were built on speculation, the owner would usually know the ultimate occupancy of the space but might not know the actual tenants. For this type of building, the owner has several compliance choices:
1. Declare building to be unconditioned space, forcing tenants to be responsible for envelope, interior lighting, possibly some exterior lighting, and mechanical compliance. This option may be very costly as most envelope and mechanical measures are far more expensive when they are installed in the building after the shell is completed (see discussion below).
2. Include envelope compliance as well as mechanical and/or lighting compliance, when those systems are to be installed prior to leasing.
There are several potential pitfalls with delaying envelope compliance. For example, tenants may have a difficult time showing compliance, depending on fenestration areas and glass efficiency. An energy code update between the time of shell construction and energy compliance for a tenant improvement could make compliance even more difficult. Constructing a “big box” style building without skylights, where skylights are required under the prescriptive approach, will also create a compliance challenge (and possibly impose large costs to retrofit skylights). In most instances upgrading the envelope later increases total construction costs, as it is easier to install envelope features at time of construction of the shell than afterwards. And for buildings that are certain to be conditioned, some enforcement agencies require envelope compliance at the time of shell construction.
For information about energy compliance for tenant improvements in existing buildings, see Section 1.7.12.
An obvious example is declaring the shell to be unconditioned, not insulating the shell and having to insulate the shell as part of the tenant improvement that adds air conditioning. This increases the final cost of the building and should render the shell less valuable for spaces that are ultimately going to be conditioned.
A less obvious example is the shell of a building that will ultimately become a big box retail store or a warehouse with lighting power densities greater than 0.5 W/ft², ceiling heights greater than 15 ft, and an enclosed area greater than 5,000 ft². Such occupancies are prescriptively required to have skylights and daylighting controls. Installing skylights in the roof of the speculative building shell is less expensive than retrofitting them later. This should be considered when designing speculative shell buildings for the big box retail or warehouse market, as they will be more saleable than those requiring skylight retrofits.
Because compliance may be demonstrated for each component separately, the owner can simply demonstrate that the systems being built meet the Standards. The remaining construction and Standards compliance work can be dealt with as each tenant obtains building permits for work in their individual spaces (see Section 1.7.12).
Unknown Occupancy
Speculative buildings are often built for which the ultimate occupancy is determined at the time of leasing and not during construction of the building shell. The structure, for example, could eventually be used as an office, a warehouse, a restaurant, or retail space. Because the Standards treat these occupancies in a similar fashion, the fact that the ultimate occupancy is unknown is not a significant problem. The major items affected by the ultimate occupancy have to do with lighting and ventilation requirements. If at the time of permitting a tenant is not identified for a multi-tenant space, the “All other areas” lighting power density allowances from Standards Table 140.6-C shall be used.
The major problem that can occur with this type of building comes when the owner elects to declare it as an unconditioned building and defer Standards compliance until such time as a tenant installs mechanical space conditioning equipment.
Because the Standards are different for residential, high-rise residential and nonresidential buildings, and because mixed-use buildings occasionally include more than one type of nonresidential occupancy, there is potential for confusion in application. The Standards address these circumstances regarding mixed-use buildings:
1. Mixed Low-Rise Residential and Nonresidential Occupancies. When a building includes both low-rise residential and nonresidential occupancies, the requirements are different depending upon the percentages of the conditioned floor that is occupied by each occupancy type:
i. Minor Occupancy (Exception 1 to §100.0(f)). When a residential occupancy occurs in the same building as a nonresidential occupancy, and if one of the occupancies is less than 20 percent of the total conditioned floor area, the smaller occupancy is considered a “minor” occupancy. Under this scenario, optionally, the entire building may be treated as if it is the major occupancy for the purpose of envelope, HVAC, and water heating. Lighting requirements in §140.6 through 140.8 or 150.0(k) must be met for each occupancy separately. The mandatory measures applicable to the minor occupancy, if different from the major occupancy, would still apply.
ii. Mixed Occupancy. When residential occupancy is mixed with a nonresidential occupancy, and if neither occupancy is less than 20 percent of the total conditioned floor area, these occupancies fall under different sets of Standards and must be considered separately. Two compliance submittals must be prepared, each using the calculations and forms of its respective Standards. Separate compliance for each occupancy, to their respective Standards, is an option when one of the occupancies is a minor occupancy, as discussed in the paragraph above.
2. Different Nonresidential Occupancies. When multiple occupancies, such as office, restaurant, and retail fall under the Nonresidential Standards, they would be treated under the same compliance approach as separate occupancies, such as office, restaurant, and retail occupancies. In general, all nonresidential occupancies have the same envelope requirements and can be treated the same across all nonresidential occupancies. High-rise residential and hotel-motel guest rooms have different envelope requirements from the nonresidential envelope requirements and should be treated differently. Lighting and mechanical requirements vary among the various types of space usage categories and should also be treated differently according to each occupancy type.
Hotel/Motel and Nonresidential Occupancies. A hotel/motel with guest rooms, restaurants, sports facilities and/or other nonresidential occupancies is defined as hotel/motel occupancy. The only variance is that the guestroom envelope and lighting and HVAC control requirements are different from the nonresidential occupancy energy requirements that would apply to the “common” areas of the building.
Example 1-1
Question
A 250,000 ft² high-rise office building includes a small 900 ft² apartment on the first floor for use by visiting executives. This is clearly a residential occupancy, so is the apartment required to meet the residential requirements of the Standards, and if so which ones – high rise residential or low rise residential?
Answer
No. First of all the apartment occupies less than 20 percent of the total conditioned floor area, so it is a minor occupancy and may be treated as part of the office occupancy. Secondly, since it is located on the first floor of the building it is technically a low rise residential building. As a result, all of the residential mandatory measures apply.
High-rise residential buildings (four habitable stories or more) are covered by this 'manual and the Nonresidential Standards.
The Standards apply separately to the living quarters and to other areas within the building. Living quarters are those non-public portions of the building in which a resident lives. High-rise residential dwelling units must incorporate the envelope and mechanical elements of the Nonresidential Standards, with the lighting and service hot water needs of residential buildings. Outdoor lighting, including parking lots and garages for eight or more vehicles and for indoor or outdoor signs (other than exit signs) must comply with the Nonresidential Standards. Exit signs must comply with the Appliance Efficiency Regulations.
The following subsections discuss the special compliance requirements that apply to high-rise residential occupancies.
Mandatory Measures
The mandatory measures for nonresidential envelope, mechanical, indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, and signs apply to high-rise residential buildings. Special requirements for high-rise residential buildings are summarized below:
1. Living quarters must meet the applicable indoor lighting requirements for residential buildings.
2. Outdoor lighting must meet the applicable outdoor lighting requirements of the Nonresidential Standards.
3. Indoor and outdoor signs (other than exit signs) must comply with the Nonresidential Standards. Exit signs must comply with the Appliance Efficiency Regulations.
4. High-rise residential occupancies must meet setback requirements applicable to residential occupancies.
5. Readily accessible area switching controls are not required in public areas provided switches that control the lights in public areas are accessible to authorized personnel.
6 Automatic lighting shut-off controls are not required for living quarters.
Prescriptive Compliance
The prescriptive requirements for envelope, mechanical and lighting apply to high-rise residences. The following summarize the special prescriptive requirements for high-rise residential buildings.
1. The envelope must meet the prescriptive envelope criteria for high-rise residential buildings (Standards Table 140.3-B).
2. High-rise residential living quarters are not required to have economizer controls.
3. High-rise residential living quarters are exempt from the nonresidential lighting power density requirements. However, lighting within the dwelling units must meet the lighting requirements of §150.0(k) that governs lighting in all spaces (including kitchen lighting requirements) except closets less than 70 ft² floor area. See Chapter 6 of the Residential Compliance Manual.
4. Each occupancy (other than living quarters) in the high-rise residence must comply with the Nonresidential Lighting Standards.
5. For compliance with water heating requirements, use the residential compliance.
Performance Compliance
The rules for high-rise residential performance compliance are identical to the performance compliance rules for all nonresidential buildings. The area of each function of a high-rise residence is input into the program along with its corresponding envelope, mechanical and lighting features. The compliance software will automatically calculate an energy budget for the standard design, and the proposed design's energy use.
This section discusses both the similarities and differences between the requirements for a hotel/motel and other nonresidential or high-rise residential buildings.
The design of a hotel or motel is unique in that the design must incorporate a wide variety of occupancies and functions into one structure. The occupancies range from nonresidential occupancies to hotel/motel guest rooms. Design functions that affect guests range from the "experience of arrival" created through the main lobby's architectural features to the thermal comfort of the guest rooms. Other functions that hotel/motel designs must address include restaurants, kitchens, laundry, storage, light assembly, outdoor lighting, sign lighting, and other items that are necessary to the hotel/motel function. In short, these structures can range from simple guest rooms with a small office, to a structure encompassing a small city.
Like other occupancies, compliance is submitted for the features covered in the permit application only. The nonresidential areas must meet the envelope, mechanical, indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, and sign lighting portions of the Nonresidential Standards, and the guest room portions of hotels/motels must meet the envelope, mechanical, and lighting provisions applicable only to hotels/motel guest rooms. In essence, each portion of the building individually complies with the provisions applicable to that occupancy.
Since hotel/motels are treated as a mixture of occupancies covered by the Standards, the concepts presented at the beginning of each chapter apply to hotels/motels as they would any other nonresidential occupancy.
Mandatory Measures
The mandatory measures for envelope, mechanical, indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, and sign lighting apply to hotels/motels. The following bullets describe special requirements or exceptions for hotel/motel buildings.
1. 90 percent of the hotel/motel guest rooms must meet the applicable Lighting Standards for residential buildings.
2. Outdoor lighting must meet the applicable Outdoor Lighting Standards.
3. Indoor and outdoor signs (other than exit signs) must comply with the Nonresidential Standards. Exit signs must comply with the Appliance Efficiency Regulations.
4. Hotel and motel guest room thermostats shall have numeric temperature settings.
5. Readily accessible area switching controls are not required in public areas provided switches that control the lights in public areas are accessible to authorized personnel.
6. Automatic lighting shut-off controls are not required for hotel/motel guest rooms.
Prescriptive Compliance
The prescriptive requirements for envelope, mechanical and lighting apply to hotel/motels. The following prescriptive requirements are specific to hotel/motels:
1. Hotel/motel guest rooms must meet the prescriptive envelope criteria for high-rise residential buildings rather than the prescriptive criteria for nonresidential buildings.
2. Hotel and motel guest rooms are not required to have economizer controls.
3. Guest rooms in hotel/motels are exempt from the lighting power density requirements. However, lighting must meet the residential requirements of §150.0(k).
4. Each occupancy (other than guest rooms) in the hotel/motel must comply with the Nonresidential Lighting Standards.
5. For compliance with water heating requirements, use the residential compliance.
Performance Compliance
The rules for performance compliance are identical to the rules for complying for all other nonresidential and high-rise residential buildings. The area of each function of a hotel/motel is input into the program along with its corresponding envelope, mechanical and indoor lighting features. The Computer Software program will automatically calculate an energy budget for the standard design, and the proposed design’s energy use. The proposed design must be less than or equal to the standard design for the building to comply.
Live-work buildings are a special case of mixed occupancy buildings, as they combine residential and nonresidential uses within individual units. In general, the low-rise or high-rise residential requirement (depending on the number of habitable stories) applies since these buildings operate (and therefore are conditioned) 24 hours per day. Lighting in designated workspaces is required to show compliance with the Nonresidential Lighting Standards (§140.6).
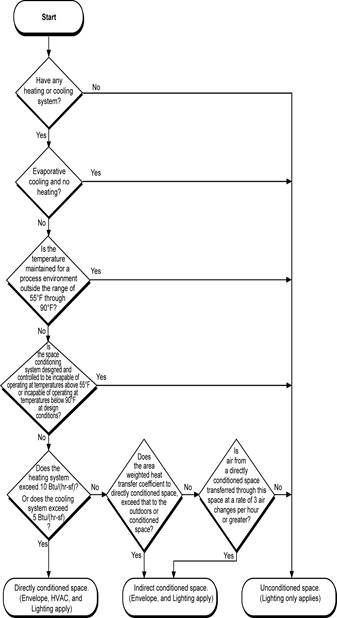
Unconditioned space is neither directly nor indirectly conditioned, as defined in section 1.7.17. Both the requirements for lighting and minimum skylight area apply to unconditioned space. Some typical examples of spaces that may be unconditioned:
A. Enclosed parking structures
B. Automotive workshops
C. Enclosed entry courts or walkways
D. Enclosed outdoor dining areas
E. Greenhouses
F. Loading docks
G. Warehouses
H. Mechanical/electrical equipment rooms
Keep in mind that these kinds of spaces are not always unconditioned. The specifics of each case must be determined. See Figure 1-1 to determine whether a space is unconditioned or conditioned.
 |
When previously unconditioned space becomes conditioned, the space is then considered an “addition” and all the building’s components must then comply as if it were a new building.
This situation has potentially significant construction and cost implications. For example, if an unconditioned warehouse is upgraded with a heating system, thus becoming conditioned space, the building envelope must comply with the current envelope requirements and the lighting system must be brought into conformance with the current lighting requirements, including mandatory wiring and switching. If the envelope has large windows, it is conceivable that some would have to be eliminated or replaced with more efficient windows. If the lighting system is inefficient, fixtures might have to be removed and new, more efficient fixtures installed.
This requirement can cause difficulty when an owner of a building seeks exemption from complying with the Standards by erecting a shell with no plans to condition it. For example, the owner of an office building obtains a permit for the structure and envelope, but wishes to leave the space conditioning and lighting improvements to the tenants. If that owner claims unconditioned status for that building, the owner does not have to demonstrate compliance with the envelope requirements of the Standards, but does have to demonstrate compliance with the lighting requirements. If at the time of permitting a tenant is not identified for a multi-tenant space, the “All other areas” lighting power density allowances from Standards Table 140.6-C shall be used. As soon as the tenant applies for a permit to install the HVAC equipment, however, the envelope and any existing lighting to remain must then be brought into full compliance with the requirements for the occupancy designated at the time of the HVAC permit application. This is the only circumstance when systems, other than those subject to the current permit application, fall under the Standards. If the building was initially designed in a way that makes this envelope compliance difficult, the building envelope may require expensive alterations to bring it into compliance.
Many enforcement agencies require the owner to sign an affidavit at the time of the initial building permit for the shell, acknowledging the potential difficulties of future envelope or lighting compliance.
To minimize Standards compliance difficulties, the recommended practice is to demonstrate energy compliance at the time the envelope is built, and to demonstrate compliance for the lighting systems when lighting systems are installed.
Tenant improvements, including alterations and repairs, may be considered new construction in an existing building. For example, the base building has been constructed, but the individual tenant spaces have not been completed. Tenant improvements can include work on the envelope, the mechanical, or the lighting systems. Whatever the case, the system or systems being installed are considered to be new construction, and must comply with some or all of the current Standards, depending on the extent of the changes (see following sections).
The only circumstance when systems other than those subject to the current permit application come under scrutiny is when the tenant improvement results in the conditioning of previously unconditioned space.
An alteration is any change to a building’s water heating system, space conditioning system, indoor lighting system, outdoor lighting system, sign, or envelope that is not an addition. Additions are discussed in §141.0(a). Alterations or renovations to existing conditioned spaces have their own set of rules for energy compliance. They are covered in §141.0(b).
In summary, the alteration rules are:
1. The Standards apply only to those portions or components of the systems being altered (altered component); untouched portions or components need not comply with the Standards.
2. If an indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, or sign lighting alteration increases the energy use of the altered systems, the alteration must comply with the current Standards.
3. Alterations must comply with the mandatory measures for the altered components.
4. New systems in the alteration must comply with the current Standards.
5. In an existing unconditioned building, outdoor lighting, or sign lighting system, altered lighting must meet mandatory measures for the altered lighting component.
6. Alterations that increase the connected lighting load or replace more than 10 percent of the lighting fixtures (counting existing and new fixtures only in the enclosed spaces where light fixture alterations are proposed) must meet §141.0(b)jii .
7. Alteration that replace more than 50 percent of the luminaires shall comply with §141.0(b)jiii
8. Replacement of parts of an existing lighting fixture, including installing new ballasts or lamps, without replacing the entire luminaires is not an alteration.
9. In an existing unconditioned building, where evaporative cooling is added to the existing unaltered envelope and lighting, does not need to be brought into compliance with current Standards.
10. Mechanical system alterations are governed primarily by the mandatory measures.
Beyond meeting all mandatory requirements, alterations must also comply either with applicable prescriptive requirements discussed in Chapters 3 through 8; or must comply using the performance path. Within the performance approach, changes to the existing building, such that the entire building (existing and alteration) may comply as explained in Section 3.7 and Chapter 11. Keep in mind that performance credit is given only for systems that are actually changed under the current permitted scope of work.
Example 1-2
Question
An owner wants to add less than 50 ft² of new glazing in an old nonresidential building in climate zone 3. What are the applicable requirements for the new glazing?
Answer
Exception to §141.0(b)2Ai exempts up to 50 ft² of added windows from the RSHGC and VT requirements in Table 141.0-A. Therefore, the new glazing must meet only the climate zone 3 U-factor requirement of 0.58.
Example 1-3
Question
A building owner wants to change existing lighting fixtures with new ones. Do the Standards restrict the change in any way?
Answer
If more than 10 percent of the fixtures are replaced in the permitted space (excluding enclosed spaces where no new lighting fixtures are proposed), or the connected load is increased, the Standards will treat this as a new lighting system that must comply with §141.0(b)2I. Any applicable mandatory requirement affected by the alteration applies, and the mandatory switching requirements would apply to the improved system if the circuiting were altered. Appliance Efficiency Regulations requirements for ballasts would also apply.
Example 1-4
Question
A building owner wants to rearrange some interior partitions and re-position the light fixtures in the affected rooms. Do the Standards apply to the work?
Answer
Each of the newly arranged rooms must have its own light switches. Since there is no change in the connected lighting load or the exterior envelope, only the mandatory light switching requirements would apply.
Example 1-5
Question
A building owner wants to rearrange some duct work and add some additional fan coils to an existing HVAC system to improve comfort. Do the Standards apply to the work?
Answer
There would be no change in the load on the system nor any increase in its overall capacity, so the Standards would not apply to the central system. Only the duct construction requirements apply to altered ducting.
Example 1-6
Question
A building owner wants to replace an existing chiller. No other changes will be made to the HVAC system. Do the Standards restrict the change in any way?
Answer
The mandatory efficiency requirements would govern the efficiency of the new chiller. The other parts of the system are unchanged and therefore unaffected by the Standards.
Example 1-7
Question
A building has a high ceiling space and the owner wants to build a new mezzanine space within it. There will be no changes to the building envelope or to the central HVAC system. There will be new lighting installed. How do the Standards apply?
Answer
Since a mezzanine does not add volume, it is an alteration, not an addition. The existing systems are not affected unless they are altered. The new lighting must comply with all requirements of the Standards. The envelope is unchanged, so there are no requirements for it. The mechanical system duct work is simply extended without increase in system capacity, so only the duct construction and insulation requirements apply.
An addition is any change to a building that increases floor area and conditioned volume. Additions involve either the construction of new, conditioned space and conditioned volume, the installation of space conditioning in a previously unconditioned space, or the addition of unconditioned space. The mandatory measures and either the prescriptive or the performance requirements apply. For conditioned space, the heating, lighting, envelope, and water heating systems of additions are treated the same as for new buildings. The only exception to this is if the existing mechanical system(s) are simply extended into the addition: Exception to §141.0(a). Refer above to Section 1.7.11 for further discussion of previously unconditioned space. Note that unconditioned additions need only comply with indoor, outdoor lighting, and sign lighting requirements of the Standards.
There are three options for the energy compliance of additions under the Standards:
Treat the addition as a stand-alone building with adiabatic walls to conditioned space (§141.0(a)1 and §141.0(a)2Bi). This option can employ either the prescriptive or the performance approach. Adiabatic means the common walls are assumed to have no heat transfer between the addition and the adjacent conditioned space, and are ignored entirely.
Model the combination of existing building with the addition (§141.0(a)2Bii). This is a performance approach option only. Under this scenario, the proposed energy use is calculated based on existing building features that remain unaltered and all alterations (actual values of the proposed alterations) plus the proposed addition. The standard design (allowed) energy budget is calculated based on:
1) The existing building features that remain unaltered; and
2) All altered features modeled to meet requirements of §141.0(b); and,
3) The addition modeled to meet requirements of §141.0(a)1.
If the proposed building energy use is less than or equal to the standard design energy budget, then the building complies. The standard design for any alterations to the existing lighting or mechanical systems is based on the requirements for altered systems in §141.0(b).
This compliance option will generally ease the energy requirements of the addition only if there are energy improvements to the existing building. It may allow the designer to make a relatively energy inefficient addition comply depending on the nature and scope of the energy improvements to the existing building.
The existing structure combined with the addition can be shown to comply as a whole building meeting all requirements of the Standards for new construction for envelope, lighting and mechanical. This method is only practical if the existing building is at or will be improved to the overall level of the current Standards.
Example 1-8
Question
A restaurant adds a conditioned greenhouse-style dining area with very large areas of glazing. How can it comply with the Standards?
Answer
Because of its large glass area, it will not comply on its own. By making substantial energy improvements to the existing building (envelope, lighting and mechanical features), or by upgrading the existing building so that the entire building meets the requirements for new construction, it is possible for the combined building to comply. The performance approach would be used to model the entire building as an existing-plus-addition.
To accumulate enough energy credit that can be used to offset (trade off against) the large glazing area in the addition, several design strategies are available including:
1) Envelope improvements to the existing building which exceed the performance of the requirements in §141.0(b)1 and §141.0(b)2A and B; and/or
2) New indoor lighting in the existing building which has a lower Installed LPD (Lighting Power Density) than the Allowed LPD in §140.6; and/or,
3) Existing building
mechanical system improvements that exceed the requirements of §141.0(b)2C, D
and E.
A change of occupancy alone does not require any action under the Standards. If changes (alterations) are made to the building, however, then the rules for alterations or additions apply (see Sections 1.7.13 and1.7.14).
If the change in occupancy involves converting from a residential to a nonresidential occupancy or vice versa (changes defined by the California Building Code occupancy definitions), then the Standards applicable to the new occupancy would govern any alterations made to the building. For example, if a home is converted to law offices, and a new lighting system is installed, the Nonresidential Lighting Standards would apply. If a new HVAC system is installed, all the nonresidential HVAC requirements would have to be met.
If no changes are proposed for the building, it is advisable to consider the ventilation requirements of the new occupancy. For example, if a residence is converted to a hair salon, the ventilation rates of the building should be considered. With new sources of indoor pollution, the existing residential ventilation rates would likely not be adequate for the new uses. However, no change is required by the energy standards.
A repair is the reconstruction or renewal of any part of an existing building for the purpose of its maintenance. Repairs shall not increase the preexisting energy consumption of the required component, system, or equipment.
This section explains the definitions and terms necessary for understanding the scope and application of the Nonresidential Standards. In most cases, a careful reading of these definitions will resolve questions of interpretation. See also the Glossary in Reference Joint Appendix JA1.
Building is any structure or space that is covered by §100.0. By this definition, a building is not necessarily a complete physical structure. For the Standards, a building in this sense can be a lighting system recircuiting project, because this would require an electrical permit.
Conditioned Floor Area (CFA) is the floor area (in ft²) of enclosed conditioned space on all floors of a building, as measured at the floor level of the exterior surfaces of exterior walls enclosing the conditioned space. Once the spaces that are directly or indirectly conditioned are identified, then it is possible to calculate the conditioned floor area of the building. This number is used for various calculation purposes in complying with the Standards. The CFA is generally calculated from dimensions on the floor plans of the building. It is measured from the outside surfaces of exterior walls, with the dimensions taken at floor level. This definition helps mitigate any complexity from sloping walls, bay windows and other unique building details.
Conditioned Space is space in a building that is either directly conditioned or indirectly conditioned. In most circumstances it is obvious whether a space is conditioned or unconditioned. There are, however, special circumstances that require a closer look at the definitions of directly and indirectly conditioned space.
Space-conditioning system may consist of but is not limited to chiller/compressor, air handler unit, cooling and heating coils, air and water cooled condenser, economizer, and the air distribution systems, which provide either collectively or individually heating, ventilation, or cooling within or associated with conditioned spaces in a building.
Directly Conditioned Space is an enclosed space that is provided with wood heating, is provided with mechanical heating that has a capacity exceeding 10 Btu/(hr. × ft.²), or is provided with mechanical cooling that has a capacity exceeding 5 Btu/(hr. × ft.²)., unless the space-conditioning system is designed for a process space or process load. Directly Conditioned Spaces may be only mechanically heated or mechanically cooled space excluding any process loads(discussed below), i.e., it does not have to be both heated and cooled. Also, it depends on how much heating or cooling is provided to determine if the space is directly conditioned. It is not uncommon for an otherwise unheated space (such as a warehouse) to have a small area with a unit heater, such as a desk on the loading dock. This usually does not make the entire structure a heated space. For a space to be considered directly conditioned, the total quantity of heating provided to the space has to exceed 10 Btu/(hr-ft²), excluding any contributions from process loads. For cooling, the mechanical system must provides more than 5 Btu/(hr-ft²), for the space to be considered directly conditioned, excluding any contributions from process loads.
Process Space is a space that is thermostatically controlled to maintain a process environment temperature less than 55°F or to maintain a process environment temperature greater than 90°F for the whole space that the system serves, or is a space within a space-conditioning system designed and controlled to be incapable of operating at temperatures above 55°F or incapable of operating at temperature below 90°F unless the space conditioning is designed and controlled to be incapable of operating at temperatures above 55°F or incapable of operating at temperatures below 90°F at design conditions. These definitions contain several key ideas central to the Standards
Process is an activity or treatment that is not related to the space conditioning, lighting, service water heating, or ventilating of a building as it relates to human occupancy. Covered Processes are processes that are regulated under Part 6 which include but are not limited to computer rooms, laboratory exhaust, garage exhaust, commercial kitchen ventilation, refrigerated warehouses, supermarket refrigeration systems, compressed air systems, process boilers. The spaces that include the Covered Process loads must meet the HVAC efficiency requirements in §110.1 and §110.2 as well as the appropriate mandatory requirements in §120.6 and prescriptive requirements in §140.6.
Enclosed Space is space that is substantially surrounded by solid surfaces such as walls, ceilings or roofs, doors, fenestration areas, and floors or ground. Spaces that are not enclosed are spaces that are open to the outdoors, such as covered walkways, parking structures that are open or have fenced mechanical enclosures.
Entire Building is the ensemble of all enclosed space in a building, including the space for which a permit is sought, plus all existing conditioned and unconditioned space within the structure. This definition affects lighting compliance within the complete building method.
Habitable Story is a story that contains space in which humans may work or live in reasonable comfort, and that has at least 50 percent of its volume above grade. This definition is important in distinguishing between high-rise and low-rise residential buildings, which are covered by different Standards and are described in separate manuals. Basement floors with more than 50 percent of their volume below grade are not counted as habitable stories regardless of their actual use. In buildings on sloping ground, the calculation of volume below grade can become cumbersome, but for most buildings it will be obvious whether the floor is at least 50 percent above grade.
Indirectly Conditioned Space is enclosed space including, but not limited to, unconditioned volume in atria, that (1) is not directly conditioned space; and (2) either (a) has an area-weighted heat transfer coefficient to directly conditioned space exceeding that to the outdoors or to unconditioned space, or, (b) is a space through which air from directly conditioned spaces is transferred at a rate exceeding three air changes per hour. This definition is important because the Standards treat indirectly conditioned space the same as conditioned space; in other words, indirectly conditioned spaces must meet the requirements of the Standards. As a guide, professional judgment should be exercised when determining whether a space is indirectly conditioned, especially as it relates to door placement in the space. When an enclosed space that is not directly conditioned has openings only into a conditioned space, it should be considered indirectly conditioned. Likewise, when an enclosed space that is not directly conditioned has openings only to the outdoors, it should be considered to be unconditioned. When enclosed spaces that are not directly conditioned have openings both to the outdoors and to conditioned spaces, an evaluation of relative heat transfer and air change rate (UA) should be used to determine the status of the space. A typical example of an indirectly conditioned space might be the stairwell of a high-rise office building. The first part of the definition is that it not be directly conditioned. This is not uncommon in stairwells. The second part of the definition is that it be provided with space conditioning energy from a space that is directly conditioned. This can be done in one of two ways. The first is by conduction heat transfer. If heat is transferred in from directly conditioned space (e.g., through the walls of the stairwell) faster than it is transferred out to the unconditioned surroundings, then the space is considered to be indirectly conditioned. The second way is for the space to be ventilated with air from directly conditioned spaces. For example, if exhaust hoods draw air through a kitchen from the dining room at a rate exceeding three air changes per hour, then the kitchen will be considered indirectly conditioned space.
Mechanical Cooling is lowering the temperature within a space using refrigerant compressors or absorbers, desiccant dehumidifiers, or other systems that require energy from depletable sources to directly condition the space. In nonresidential, high-rise residential, and hotel/motel buildings, cooling of a space by direct or indirect evaporation of water alone is not considered mechanical cooling (see also “directly conditioned space”). For buildings covered by this manual, evaporative cooling is not considered mechanical cooling. This means, for example, that a warehouse with only evaporative coolers does not meet the definition of mechanical cooling. Nonresidential buildings with evaporate cooling are unconditioned spaces.
Mechanical Heating is raising the temperature within a space using electric resistance heaters, fossil fuel burners, heat pumps, or other systems that require energy from depletable sources to directly condition the space. If the only source of the heat is a nondepletable source, then the system is not considered mechanical heating. Nondepletable sources would include solar collectors, geothermal sources, and heat recovered from a process, such as refrigeration chillers.
Unconditioned Space is enclosed space within a building that is not directly conditioned or indirectly conditioned space. Unconditioned spaces are required to meet the Indoor Lighting Standards.
High-Rise Residential is a building, other than a
hotel/motel, of occupancy group
R-1 with four or more habitable stories.
California Building Code Occupancy Group
R-1 includes apartment houses,
convents and monasteries (accommodating more than 10 persons). (See definition
of Unconditioned Space above). If a building has four or more habitable stories,
any residential occupancy in the building is considered high-rise residential,
regardless of the number of stories that are residential.
Hotel/Motel is a building or buildings incorporating six or more guest rooms or a lobby serving six or more guest rooms, where the guest rooms are intended or designed to be used, or which are used, rented, or hired out to be occupied, or which are occupied for sleeping purposes by guests, and all conditioned spaces within the same building envelope. Hotel/motel also includes all conditioned spaces that are (1) on the same property as the hotel/motel, (2) served by the same central HVAC system as the hotel/motel, and (3) integrally related to the functioning of the hotel/motel as such, including, but not limited to, exhibition facilities, meeting and conference facilities, food service facilities, lobbies and laundries. A key part of this definition is that the hotel/motel includes all spaces within the same building envelope as the lobby or the guest rooms. This is because hotel/motel buildings are generally multi-purpose facilities. They may include such diverse spaces as restaurants, auditoriums, retail stores, offices, kitchens, laundries and swimming pools. All are treated as hotel/motel spaces. For hotels/motels with five or less guest rooms, low-rise residential compliance should be used instead of nonresidential compliance. All hotels/motels should use the low-rise residential water heating calculation approach.
This concept extends to other buildings associated with the hotel/motel that pass the three tests:
•Same property.
•Same central HVAC system.
•Integrally related to the hotel/motel.
Mixed Occupancies. The Standards apply to mixed occupancies in the same way they apply to single occupancy buildings. The Residential Standards apply to applicable occupancies; the Nonresidential Standards apply to appropriate occupancies. If these two types occur in the same building, the building must be treated as two separate buildings for purposes of energy compliance, with each part meeting its applicable requirements. An exception provides that if one occupancy makes up 80 percent of the building, the entire building may comply with the envelope and mechanical provisions of the dominant occupancy. The interior lighting requirements and mandatory measures for the actual occupancy will apply.
Other Occupancy Definitions. There are over 35 additional occupancy definitions in the Standards. They are used primarily to assign lighting area categories. Refer to the Glossary in Reference Joint Appendix JA1 for these definitions (found alphabetically under “Occupancy Type)”.
Example 1-9
Question
If a space were 1,000 ft², how large would the heating system have to be to make the space directly conditioned?
Answer
The heating system would have to be larger than 10 Btu/(hr-ft²) x 1,000 ft² = 10,000 Btu/hr output to meet the definition of directly conditioned space.
Example 1-10
Question
A water treatment plant has a heating system installed to prevent pipes from freezing. The heating system exceeds 10 Btu/(hr-ft²) and operates to keep the space temperature from falling below 50°F. Is this plant directly conditioned?
Answer
Not if the heating system is sized to meet the building load at 50°F and is thermostatically controlled to prevent operating temperatures above 50°F. The definition of directly conditioned space excludes Process Spaces that have space conditioning designed and controlled to be incapable of operating at temperatures above 55°F at design conditions. Under these conditions, the space is not directly conditioned.
Example 1-11
Question
A process load in a manufacturing facility is generating heat inside the building shell. The manufacturing facility will install space cooling to keep the temperature from exceeding 90°F. If the thermostat will not allow cooling below 90°F (in other words, the temperature is kept at 90°F all the time), is this facility directly conditioned, if the mechanical cooling exceeds 5 Btuh/hr-ft2?
Answer
No, this facility is not a Directly Conditioned Space. The definition of Directly Conditioned Space excludes spaces where the space conditioning system is designed and controlled to be incapable of operating at temperatures below 90°F at design conditions.
Example 1-12
Question
A natural gas kiln in a factory is located within the building shell and its capacity exceeds 10 Btu/(hr-ft²). Is the space within the shell considered directly conditioned space if there is no HVAC system installed in the building?
Answer
No, since the heat from the kiln is an Exempt Process Load and not part of heat that is transferred across
the building envelope components, and there is no HVAC system installed, the space is not considered a Directly Conditioned Space and the shell does not have to meet the Standards envelope requirements; however, the space must still meet the lighting requirements of the Standards.
Example 1-13
Question
If in example above mechanical cooling with the capacity that exceeds 5 Btuh/hr-ft2 is added to the building to keep the temperature from exceeding 85°F, does the space considered directly conditioned and must the envelope meet the Standards requirements?
Answer
No, the definition of Directly Conditioned Space excludes conditioning for Process Loads.
Example 1-12
Question
If a computer room is cooled with the capacity that exceeds 5 Btuh/hr-ft2 and is controlled to a temperature of 75°F, does the space have to meet the envelope requirement of the Standards?
Answer
No. Computer rooms are a Covered Process. There are no envelope requirements in either §120.6 or §140.9.
Example 1-13
Question
The accompanying sketch shows a building with three unconditioned spaces (none has a direct source of mechanical heating or cooling). The air transfer rate from the adjacent conditioned spaces is less than three air changes per hour. The area weighted heat transfer coefficients of the walls (UA) are shown on the sketch. The roof/ceiling area weighted heat transfer coefficients (UA) for each of the three unconditioned spaces is 90 Btu/Hr -°F.
Are any of these spaces indirectly conditioned?
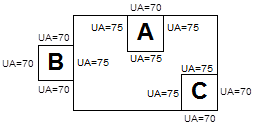
Answer
Because the air change rate is low, we evaluate each space on the basis of heat transfer coefficients through the walls and roof. It is further assumed that the floors are adiabatic. Therefore, the heat transfer will be proportional to the area weighted heat transfer coefficients of the walls and roof/ceilings.
SPACE A: The area weighted heat transfer coefficient to directly conditioned space is 3 x (75 Btu/Hr-°F) = 225 Btu/Hr-°F. The area weighted heat transfer coefficient to the outdoors or to unconditioned space is 70 Btu/Hr-°F + 90 Btu/Hr-°F = 160 Btu/Hr-°F. Since the heat transfer coefficient from Space A to the conditioned space is greater than heat transfer coefficient from Space A to outside, Space A is considered indirectly conditioned.
SPACE B: The area weighted heat transfer coefficient to directly conditioned space is 75 Btu/Hr-°F. The area weighted heat transfer coefficient to the outdoors or to unconditioned space is (3 x 70 Btu/Hr-°F) + 90 Btu/Hr-°F = 300 Btu/Hr-°F. Since the heat transfer coefficient from Space B to the conditioned space is less than the heat transfer coefficient from Space B to outside, Space B is considered unconditioned.
SPACE C: The area weighted heat transfer coefficient to directly conditioned space is (2 x 75 Btu/Hr-°F = 150 Btu/Hr-°F. The area weighted heat transfer coefficient to the outdoors or to unconditioned space is (2 x 70 Btu/Hr-°F) + 90 Btu/Hr-°F = 230 Btu/Hr-°F. Since the heat transfer coefficient from Space C to the conditioned space is less than the heat transfer coefficient from Space C to outside, Space C is considered unconditioned.
Example 1-14
Question
In a four-story building, first floor is retail, second and third floors are offices, and the fourth floor is residential (as defined in the CBC). Is the residential space high-rise or low-rise?
Answer
It is a high-rise residential space. Even though there is only one floor of residential occupancy, the building has four habitable stories, making it a high-rise building.