Requirements for PV systems and battery storage systems are dependent on the number of stories of the building. Multifamily buildings with three or fewer habitable stories have different requirements than multifamily buildings more with four or more habitable stories. Modeling software will calculate PV system and battery storage systems based on the number of habitable stories of the buildings
The PV requirements are applicable to newly constructed multifamily buildings three habitable stories or less. PV system details are based on the publicly available system calculations codes from PVWatts, which is a web application developed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, or similar calculation method approved by the Energy Commission. See Appendix F. for more information.
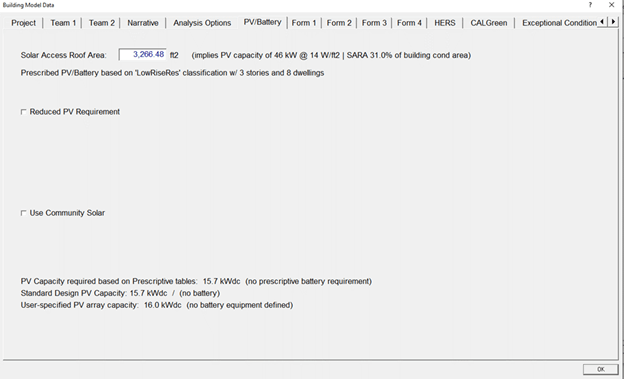
PHOTOVOLTAICS STANDARD DESIGN THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
The standard design PV system is based on requirements in 2022 Title 24 Part 6, Section 170.2(f) for multifamily buildings – three habitable stories or fewer.
For PV calculations, the software applies the CFI orientation of 170 degrees, standard efficiency for modules, inverter efficiency of 96%, fixed tracking, standard (excluding horizon) shading, roof tilt of 22.61 degrees (5:12 pitch), and annual solar access percentage of 98%.
PHOTOVOLTAICS PROPOSED DESIGN THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
For PV sizing calculations, the compliance software includes user-defined values for:
- Array orientation, including CFI1 (installation of 150–270 degrees), CFI2 (installation of 105-300 degrees), or the actual orientation.
- Module type, including standard (for example, poly- or monocrystalline silicon modules), premium (for example, high-efficiency monocrystalline silicon modules with anti-reflective coatings), or thin film (in other words, low efficiency such as 11 percent).
- Inverter efficiency.
- Array tilt in degrees or roof pitch, or CFI1 or CFI2 (installation up to 7:12).
- Array tracking type including fixed, single-axis tracking, and two-axis tracking.
- Annual solar access percentage, excluding horizon shading, of the modules.
The PV size is reported in kWdc.
COMMUNITY SOLAR THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
For projects that use an approved Neighborhood Solar Shares (NSS) program to provide the required PV, approved compliance software must determine and report the amount (PV kWdc) needed to offset the standard design PV system TDV.
Figure 12: Community Solar
Source: California Energy Commission
EXCEPTIONS TO THE PV REQUIREMENTS THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
- No PV system is required if the solar access roof area (SARA) is less than 80 contiguous square feet. SARA of the building is described in §170.2(f) of the Energy Code.
- No PV system is required when the minimum PV system size specified by §170.2(f) of the Energy Code is less than 1.8 kWdc.
- Buildings with enforcement-authority-approved roof designs, where the enforcement authority determines it is not possible for the PV system, including panels, modules and components and supports and attachments to the roof structure, to meet the requirements of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), Standard 7-16, Chapter 7, Snow Loads.
- For buildings that are approved by the local planning department prior to January 1, 2020, with mandatory conditions for approval, shading from roof designs and configurations for steep-sloped roofs, which are required by the mandatory conditions for approval, shall be considered for the annual solar access calculations and roof areas that are not allowed by the mandatory conditions for approval to have PVs shall not be considered in determining the SARA.
- PV system sizes determined using Equation 170.2-C may be reduced by 25 percent if installed in conjunction with battery storage system. The battery storage system shall meet the qualification requirements specified in Joint Appendix JA12 and have a minimum usable capacity of 7.5 kWh.
When the solar electric generation system meets one of the prescriptive exceptions, the standard design is modeled with an appropriately sized PV system. The proposed design is modeled with a system size that does not exceed the PV size required by the standard design.
BATTERY STORAGE THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
Detailed calculations for PV and battery storage are included in Appendices C and D.
The compliance software provides credit for a battery storage system coupled with a PV array or simulated as standalone. If specified, the battery storage size must be 5 kWh or larger. For Part 6 compliance, PV has no impact on energy efficiency requirements or the efficiency TDV unless a battery storage system is included and the self-utilization credit is modeled.
Including a battery storage system allows downsizing the PV system to reach a specific TDV target.
BATTERY CONTROLS THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
The three control options available, which are described in Reference Appendix Joint Appendix 12, are:
- Basic (Default Control). A simple control strategy that provides a modest credit. The compliance software assumes that the batteries are charged anytime PV generation (generation) is greater than the house load (load); conversely, the batteries are discharged when load exceeds generation. This control strategy does not allow the batteries to discharge into the grid.
- Time of Use. To qualify for the TOU control, the battery storage system shall be installed in the default operation mode to allow charging from an on-site PV system or from the utility grid if a standalone battery storage system. The battery storage system shall begin discharging during the highest-priced TOU hours of the day. This option allows discharging directly into the grid.
- Advanced DR Control. To qualify for the advanced demand response control, the battery storage system shall be programmed by default as basic control or TOU control, as described above. The battery storage control shall meet the demand-responsive control requirements specified in §110.12(a). The battery storage system shall have the capability to change the charging and discharging periods in response to signals from the local utility or a third-party aggregator. Upon receiving a demand response signal from a grid operator, this option allows discharging directly into the grid.
Qualification for battery storage systems is described in Reference Appendices, Joint Appendix JA12.
VERIFICATION AND REPORTING THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
PV required size and battery system storage details are reported as special features on the LMCC.
SELF-UTILIZATION CREDIT THREE HABITABLE STORIES OR LESS
The 2022 Energy Code do not allow a tradeoff between the Efficiency TDV and the effect of PV on the Total TDV unless battery storage is provided. When the PV system is coupled with at least a 5 kWh battery storage system, the compliance software allows a portion of the PV/flexibility TDV to be traded against the Efficiency TDV. A modest self-utilization credit can be used for tradeoffs against building envelope and efficiencies of the equipment installed in the building. A checkbox is provided in the compliance software to enable this credit.
The magnitude of the credit is equal to the 90 percent of the difference between the 2022 and 2016 Standards envelope requirements, including:
- Below-deck batt roof insulation value of R-19 for the 2022 Standards, and R-13 for the 2016 Standard.
- Wall U-factor of 0.048 for the 2022 Standards, and U-factor of 0.051 for the 2016 Standards.
- Window U-factor of 0.30 for the 2022 Standards, and window U-factor of 0.32 for the 2016 Standards.
- In cooling climate zones, window SHGC of 0.23 for the 2022 Standards, and 0.25 for the 2016 Standards.
- QII requirement in the 2022 standards, and no QII requirements in the 2016 Standards.
|
Climate Zone
|
Multifamily
|
|
01
|
10%
|
|
02
|
7%
|
|
03
|
6%
|
|
04
|
8%
|
|
05
|
5%
|
|
06
|
3%
|
|
07
|
2%
|
|
08
|
6%
|
|
09
|
7%
|
|
10
|
6%
|
|
11
|
8%
|
|
12
|
9%
|
|
13
|
8%
|
|
14
|
8%
|
|
15
|
6%
|
|
16
|
8%
|
Source: California Energy Commission
The PV system and battery storage system requirements in this chapter are applicable to newly constructed multifamily buildings Four or more habitable stories. PV system details are based on the publicly available system calculation from PVWatts, which is a web application developed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, or similar calculation method approved by the Energy Commission. See Appendix F. for more information.
PHOTOVOLTAICS STANDARD DESIGN FOUR OR MORE HABITABLE STORIES
For multifamily buildings four or more habitable stories and mixed occupancy buildings four or more habitable stories with at least 80 percent of the floor area used for residential occupancy, a newly installed PV system meeting the minimum qualification requirements of Reference Joint Appendix JA11 is required. The PV size in kWdc is the smaller of the PV system size determined by Equation 170.2-D, or the total of all available SARA multiplied by 14 W/ft2 , where the PV capacity factor of Equation 170.2-D is determined by individual space function. The mapping of space function to PV or battery building type used to determine capacity factors is documented in Appendix C.
PHOTOVOLTAICS PROPOSED DESIGN FOUR OR MORE HABITABLE STORIES
For PV calculations, the compliance software includes user-defined values for:
-
Array orientation, including CFI1 (installation of 150–270 degrees, CFI2 (installation of 105-300), or the actual orientation.
-
Module type, including standard (for example, poly- or monocrystalline silicon modules), premium (for example, high-efficiency monocrystalline silicon modules with anti-reflective coatings), or thin film (in other words, low efficiency such as 11 percent).
-
Inverter efficiency.
-
Array tilt in degrees or roof pitch, or CFI1 or CFI2 (installation up to 7:12).
-
Array tracking type including fixed, single-axis tracking, and two-axis tracking.
-
Annual solar access percentage, excluding horizon shading, of the modules.
The PV size is reported in kWdc.
EXCEPTIONS TO THE PV REQUIREMENTS MORE THAN THREE HABITABLE STORIES
-
No PV system is required if the total solar access roof area (SARA) is less than three percent of the conditioned floor area. SARA of the building is described in §170.2(g) of the Energy Code.
-
No PV system is required when the minimum PV system size specified by §170.2(g) of the Energy Code is less than 4 kWdc.
-
No PV system is required if the solar access roof area (SARA) is less than 80 contiguous square feet.
-
Buildings with enforcement-authority-approved roof designs, where the enforcement authority determines it is not possible for the PV system, including panels, modules and components and supports and attachments to the roof structure, to meet the requirements of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), Standard 7-16, Chapter 7, Snow Loads.
-
Multi-tenant buildings in areas where a load serving entity does not provide either a Virtual Net Energy Metering or community solar program.
When the solar electric generation system meets one of the prescriptive exceptions, the standard design is modeled with an appropriately sized PV system. The proposed design is modeled with a system size that does not exceed the PV size required by the standard design.
BATTERY STORAGE STANDARD DESIGN MORE THAN THREE HABITABLE STORIES
For multifamily buildings more than three habitable stories that are required to have a PV System through §170.2(g), a battery storage system meeting qualification requirements of Reference Joint Appendix JA12 is also required. The battery system capacity and rated power is determined by Equation 170.2-E and Equation 170.2-F respectively, where the storage capacity and power factors of these equations is determined by individual space function. The mapping of space function to PV or battery building type used to determine capacity factors is documented in Appendix C.
BATTERY STORAGE PROPOSED DESIGN MORE THAN THREE HABITABLE STORIES
Detailed calculations for PV and battery storage are included in Appendices C and D.
The compliance software provides credit for a battery storage system coupled with a PV array. If specified, the battery storage size must be 5 kWh or larger. For Part 6 compliance, PV has no impact on energy efficiency requirements or the efficiency TDV unless a battery storage system is included and the self-utilization credit is modeled.
Including a battery storage system allows downsizing the PV system to reach a specific TDV target.
Compliance software includes a checkbox option to allow excess PV generation credit for above-code programs. This option, combined with a battery storage system, allows any PV size with full TDV credit.
EXCEPTIONS TO THE BATTERY STORAGE REQUIREMENTS MORE THAN THREE HABITABLE STORIES
-
No battery storage system is required if the installed PV system size is less than 15 percent of the size determined by Equation 170.2-D.
-
No battery storage system is required when the required battery storage system rated capacity is less than 10 kWh.
-
For multi-tenant buildings, the energy capacity and power capacity of the battery storage system shall be based on the tenant spaces with more than 5,000 square feet of conditioned floor area. For single-tenant buildings with less than 5,000 square feet of conditioned floor area, no battery storage system is required.
When the solar electric generation system meets one of the prescriptive exceptions, the standard design is modeled with an appropriately sized battery storage system. The proposed design is modeled with a system size that does not exceed the battery system capacity and rated power required by the standard design.


