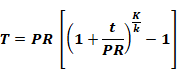Section 160.3 - Mandatory Requirements for Space Conditioning Systems in Multifamily Buildings
Space conditioning systems serving multifamily dwelling units and common use areas shall comply with the applicable requirements of Sections 160.3(a) through 160.3(c).
2. Common use area controls. Heating or cooling systems serving common use areas of multifamily buildings shall comply with application requirements of Sections 160.3(a)2A through 160.3(a)2J.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2: Heating or cooling systems exclusively serving dwelling units and common use areas providing shared provisions for living, eating, cooking, or sanitation to dwelling units that would otherwise lack these provisions may instead comply with Section 160.3(a)1.
A. Thermostatic controls for each zone. The supply of heating and cooling energy to each space-conditioning zone shall be controlled by an individual thermostatic control that responds to temperature within the zone and that meets the applicable requirements of Section 160.3(a)2B. An Energy Management Control System (EMCS) may be installed to comply with the requirements of one or more thermostatic controls if it complies with all applicable requirements for each thermostatic control.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2A: An independent perimeter heating or cooling system may serve more than one zone without individual thermostatic controls if:
i. All zones are also served by an interior cooling system; and
ii The perimeter system is designed solely to offset envelope heat losses or gains; and
iii. The perimeter system has at least one thermostatic control for each building orientation of 50 feet or more; and
iv. The perimeter system is controlled by at least one thermostat located in one of the zones served by the system.
B. Criteria for zonal thermostatic controls. The individual thermostatic controls required by Section
160.3(a)2A shall meet the following requirements as applicable:
i. Where used to control comfort heating, the thermostatic controls shall be capable of being set, locally or remotely, down to 55°F or lower.
ii. Where used to control comfort cooling, the thermostatic controls shall shall be capable of being set, locally or remotely, down to 85°F or higher.
iii. Where used to control both comfort heating and comfort cooling, the thermostatic controls shall meet Items i and ii and shall be capable of providing a temperature range or dead band of at least 5°F within which the supply of heating and cooling energy to the zone is shut off or reduced to a minimum.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2Biii: Systems with thermostats that require manual changeover between heating and cooling modes.
iv. Thermostatic controls for all single zone air conditioners and heat pumps shall comply with the requirements of Sections
110.2(c) and
110.12(a) and, if equipped with DDC to the Zone level, with the Automatic Demand Shed Controls of Section
110.12(b).
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2Biv: Package terminal air conditioners, package terminal heat pumps, room air conditioners, and room air-conditioner heat pumps.
C. Heat pump controls. All heat pumps with supplementary electric resistance heaters shall be installed with controls that comply with Section 110.2(b).
D. Shut-off and reset controls for space-conditioning systems. Each space-conditioning system shall be installed with controls that comply with the following:
i. The control shall be capable of automatically shutting off the system during periods of nonuse and shall have:
a. An automatic time switch control device complying with Section
110.9 with an accessible manual override that allows operation of the system for up to 4 hours; or
b. An occupancy sensor; or
c. A 4-hour timer that can be manually operated.
ii. The control shall automatically restart and temporarily operate the system as required to maintain:
a. A setback heating thermostat setpoint if the system provides mechanical heating; and
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2Diia: Thermostat setback controls are not required in multifamily buildings in areas where the Winter Median of Extremes outdoor air temperature determined in accordance with Section 170.2(c)1C is greater than 32°F.
b. A setup cooling thermostat setpoint if the system provides mechanical cooling.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2Diib: Thermostat setup controls are not required in multifamily buildings in areas where the Summer Design Dry Bulb 0.5 percent temperature determined in accordance with Section 170.2(c)1C is less than 100°F.
iii. Occupant sensing zone controls. Where the system providing space conditioning also provides the ventilation required by Section
160.2(c)3 and includes occupant sensor ventilation control as specified in Section
160.2(c)5E, the occupant sensing zone controls shall additionally comply with the following:
a. Occupant sensing zone controls shall comply with the Occupant Sensor Ventilation Control Device requirements of Section 160.3(c)5E and allow preoccupancy ventilation requirements of Section 160.3(c)5B; and
b. In 5 minutes or less after entering occupied-standby mode as described in Section
160.2(c)5:
I. Automatically setup the operating cooling temperature set point by 2°F or more and setback the operating heating temperature set point by 2°F or more; or
II. For multiple zone systems with Direct Digital Controls (DDC) to the zone level, setup the operating cooling temperature setpoint by 0.5°F or more and setback the operating heating temperature setpoint by 0.5°F or more.
c. In 5 minutes or less after of entering occupied-standby mode, mechanical ventilation to the zone shall remain off whenever the space temperature is between the active heating and cooling setpoints.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2Diii: Zones that are only ventilated by a natural ventilation system in accordance with Section 120.1(c)2.
EXCEPTION 1 to Sections 160.3(a)2Di, ii, and iii: Where it can be demonstrated to the satisfaction of the enforcing agency that the system serves an area that must operate continuously.
Exception 2 to Sections 160.3(a)2Di, ii and iii: Systems with full load demands of 2 kW or less, if they have a readily accessible manual shut-off switch.
E. Dampers for air supply and exhaust equipment. Outdoor air supply and exhaust equipment shall be installed with dampers that automatically close upon fan shutdown.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(a)2E: Equipment that serves an area that must operate continuously.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(a)2E: Gravity and other nonelectrical equipment that has readily accessible manual damper controls.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 160.3(a)2E: At combustion air intakes and shaft vents.
EXCEPTION 4 to Section 160.3(a)2E: Where prohibited by other provisions of law.
F. Isolation area devices. Each space-conditioning system serving multiple zones with a combined conditioned floor area of more than 25,000 square feet shall be designed, installed, and controlled to serve isolation areas.
i. Each zone, or any combination of zones not exceeding 25,000 square feet, shall be a separate isolation area.
ii. Each isolation area shall be provided with isolation devices, such as valves or dampers that allow the supply of heating or cooling to be reduced or shut-off independently of other isolation areas.
iii. Each isolation area shall be controlled by a device meeting the requirements of Section
160.3(a)2Di.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2F: Zones designed to be conditioned continuously.
G. Automatic demand shed controls. See Section
110.12 for requirements for Automatic Demand Shed Controls.
H. Economizer Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD). All newly-installed air handlers with a mechanical cooling capacity over 33,000 Btu/hr and an installed air economizer shall include a stand-alone or integrated Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD) system in accordance with Subsections
160.3(a)2Hi through
160.3(a)2Hviii.
i. The following temperature sensors shall be permanently installed to monitor system operation: outside air, supply air, and when required for differential economizer operation, a return air sensor; and
ii. Temperature sensors shall have an accuracy of ±2°F over the range of 40°F to 80°F; and
iii. The controller shall have the capability of displaying the value of each sensor; and
iv. The controller shall provide system status by indicating the following conditions:
a. Free cooling available;
d. Heating enabled, if the system is capable of heating; and
e. Mixed air low limit cycle active.
v. The unit controller shall allow manual initiation of each operating mode so that the operation of cooling systems, economizers, fans, and heating systems can be independently tested and verified; and
vi. Faults shall be reported in one of the following ways:
a. Reported to an Energy Management Control System regularly monitored by facility personnel.
b. Annunciated locally on one or more zone thermostats, or a device within five (5) feet of zone thermostat(s), clearly visible, at eye level, and meeting the following requirements:
I. On the thermostat, device, or an adjacent written sign, display instructions to contact appropriate building personnel or an HVAC technician; and
II. In buildings with multiple tenants, the annunciation shall either be within property management offices or in a common space accessible by the property or building manager.
c. Reported to a fault management application that automatically provides notification of the fault to remote HVAC service provider.
vii. The FDD system shall detect the following faults:
a. Air temperature sensor failure/fault;
b. Not economizing when it should;
c. Economizing when it should not;
d. Damper not modulating; and
viii. The FDD System shall be certified by the Energy Commission as meeting requirements of Sections
160.3(a)2Hi through
160.3(a)2Hvii in accordance with Section
110.0 and
JA6.3.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2Hviii: FDD algorithms based in Direct Digital Control systems are not required to be certified to the Energy Commission.
I. Direct Digital Controls (DDC). Direct Digital Controls to the zone shall be provided as specified by
Table 160.3-C.
i. The provided DDC system shall meet the control logic requirements of Sections
160.3(a)2E and
160.3(a)2G, and be capable of the following:
ii. Monitoring zone and system demand for fan pressure, pump pressure, heating and cooling;
iii. Transferring zone and system demand information from zones to air distribution system controllers and from air distribution systems to heating and cooling plant controllers;
iv. Automatically detecting the zones and systems that may be excessively driving the reset logic and generate an alarm or other indication to the system operator;
v. Readily allow operator removal of zone(s) from the reset algorithm;
vi. For new buildings, trending and graphically displaying input and output points; and
vii. Resetting heating and cooling setpoints in all noncritical zones upon receipt of a signal from a centralized contact or software point as described in Section
160.3(a)2G.
J. Optimum start/stop controls. Space conditioning systems with DDC to the zone level shall have optimum start/stop controls. The control algorithm shall, as a minimum, be a function of the difference between space temperature and occupied setpoint, the outdoor air temperature, and the amount of time prior to scheduled occupancy. Mass radiant floor slab systems shall incorporate floor temperature onto the optimum start algorithm.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(a)2J: Systems that must operate continuously.
A. The ASHRAE Handbook, Equipment Volume, Applications Volume, and Fundamentals Volume; or
B. The SMACNA Residential Comfort System Installation Standards Manual; or
NOTE: Heating systems are required to have a minimum heating capacity adequate to meet the minimum requirements of the CBC.
2. Design conditions. Design conditions shall be determined in accordance with the following:
B. Outdoor design conditions shall be selected from Reference Joint Appendix JA2, which is based on data from the ASHRAE Climatic Data for Region X.
C. The outdoor design temperatures for heating shall be no lower than the Heating Winter Median of Extremes values.
D. The outdoor design temperatures for cooling shall be no greater than the 1.0 percent Cooling Dry Bulb and Mean Coincident Wet Bulb values.
A. Clearances. Installed air conditioner and heat pump outdoor condensing units shall have a clearance of at least five (5) feet (1.5 meters) from the outlet of any dryer vent.
B. Liquid line drier. Installed
air conditioner and
heat pump systems shall be equipped with liquid line filter driers if required, as specified by manufacturer’s instructions.
A. Temperature rise. Central forced-air heating furnace installations shall be configured to operate in conformance with the furnace manufacturer's maximum inlet-to-outlet temperature rise specifications.
i. All air-distribution system ducts and plenums, including, but not limited to, mechanical closets and air-handler boxes, shall meet the requirements of the CMC Sections 601.0, 602.0, 603.0, 604.0, 605.0 and ANSI/SMACNA-006-2006 HVAC Duct Construction Standards Metal and Flexible 3rd Edition, incorporated herein by reference.
ii. Portions of supply-air and return-air ducts and plenums of a space heating or cooling system shall be insulated in accordance with either Subsection a or b below:
a. Ducts shall have a minimum installed level of R-6.0, or
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(b)5Aiia: Portions of the duct system located in conditioned space below the ceiling separating the occupiable space from the attic are not required to be insulated if all of the following conditions are met:
i. The non-insulated portion of the duct system is located entirely inside the building’s thermal envelope as confirmed by visual inspection.
ii. At all locations where non-insulated portions of the duct system penetrate into unconditioned space, the penetration shall be draft stopped compliant with CFC sections 703.1 and 704.1 and air-sealed to the construction materials that are penetrated, using materials compliant with CMC section E502.4.2 to prevent air infiltration into the cavity. All connections in unconditioned space are insulated to a minimum of R-6.0 as confirmed by visual inspection.
b. Ducts do not require insulation when the
duct system is located entirely in
conditioned space. For buildings with three or fewer habitable stories, duct systems located entirely in c
onditioned space shall be confirmed through field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the requirements of Reference Residential Appendix
RA3.1.4.3.8.
iii. Connections of metal ducts and the inner core of flexible ducts shall be mechanically fastened.
iv. Openings shall be sealed with mastic, tape, or other duct-closure system that meets the applicable requirements of UL 181, UL 181A or UL 181B or aerosol sealant that meets the requirements of UL 723. If mastic or tape is used to seal openings greater than 1/4 inch, the combination of mastic and either mesh or tape shall be used.
v. Building cavities, support platforms for air handlers, and plenums designed or constructed with materials other than sealed sheet metal, duct board or flexible duct shall not be used for conveying conditioned air.
Building cavities and support platforms may contain ducts. Ducts installed in cavities and support platforms shall not be compressed to cause reductions in the cross-sectional area of the ducts.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(b)5A: Ducts and fans integral to a wood heater or fireplace.
i. All factory-fabricated duct systems shall comply with UL 181 for ducts and closure systems, including collars, connections, and splices, and be labeled as complying with UL 181.
UL 181 testing may be performed by
UL laboratories or a laboratory approved by the Executive Director.
ii. All pressure-sensitive tapes, heat-activated tapes, and mastics used in the manufacture of rigid fiberglass ducts shall comply with
UL 181 and UL 181A.
iii. All pressure-sensitive tapes and mastics used with flexible ducts shall comply with
UL 181 and UL 181B.
iv. Joints and seams of duct systems and their components shall not be sealed with cloth back rubber adhesive duct tapes unless such tape is used in combination with mastic and drawbands.
i. Factory-made rigid fiberglass and flexible ducts for field-fabricated duct systems shall comply with UL 181. All pressure-sensitive tapes, mastics, aerosol sealants, or other closure systems used for installing field-fabricated duct systems shall meet the applicable requirements of UL 181, UL 181A, and UL 181B.
ii. Mastic sealants and mesh.
a. Sealants shall comply with the applicable requirements of
UL 181, UL 181A, and UL 181B, and be nontoxic and water resistant.
b. Sealants for interior applications shall be tested in accordance with ASTM C731 and D2202, incorporated herein by reference.
c. Sealants for exterior applications shall be tested in accordance with ASTM C731, C732, and D2202, incorporated herein by reference.
d. Sealants and meshes shall be rated for exterior use.
iii. Pressure-sensitive tape. Pressure-sensitive tapes shall comply with the applicable requirements of
UL 181, UL 181A, and UL 181B.
iv. Joints and seams of duct systems and their components shall not be sealed with cloth back rubber adhesive duct tapes unless such tape is used in combination with mastic and drawbands.
v. Drawbands used with flexible duct.
a. Drawbands shall be either stainless-steel worm-drive hose clamps or UV-resistant nylon duct ties.
b. Drawbands shall have a minimum tensile strength rating of 150 pounds.
c. Drawbands shall be tightened as recommended by the manufacturer with an adjustable tensioning tool.
vi. Aerosol-sealant closures.
a. Aerosol sealants shall meet the requirements of UL 723 and be applied according to manufacturer specifications.
b. Tapes or mastics used in combination with aerosol sealing shall meet the requirements of this section.
E. Duct insulation thickness. The installed thickness of duct insulation used to determine its R-value shall be determined as follows:
i. For duct board, duct liner, and factory-made rigid ducts not normally subjected to compression, the nominal insulation thickness shall be used.
ii. For duct wrap, installed thickness shall be assumed to be 75 percent (25 percent compression) of nominal thickness.
iii. For factory-made flexible air ducts, the installed thickness shall be determined by dividing the difference between the actual outside diameter and nominal inside diameter by two.
F. Duct labeling. Insulated flexible duct products installed to meet this requirement shall include labels, in maximum intervals of 3 feet, showing the thermal performance R-value for the duct insulation itself (excluding air films, vapor retarder, or other duct components), based on the tests in Section
160.3(b)5D and the installed thickness determined by Section
160.3(b)5Eiii.
G. Backdraft dampers. All fan systems, regardless of volumetric capacity, that exchange air between the building conditioned space and the outside of the building shall be provided with backdraft or automatic dampers to prevent unintended air leakage through the fan system when the
fan system is not operating.
H. Gravity ventilation dampers. All gravity ventilating systems that serve conditioned space shall be provided with either automatic or readily accessible, manually operated dampers in all openings to the outside except combustion inlet and outlet air openings and elevator shaft vents.
I. Protection of insulation. Insulation shall be protected from damage, including that due to sunlight, moisture, equipment maintenance, and wind but not limited to the following: Insulation exposed to weather shall be suitable for outdoor service (e.g., protected by aluminum, sheet metal, painted canvas, or plastic cover). Cellular foam insulation shall be protected as above or painted with a coating that is water retardant and provides shielding from solar radiation that can cause degradation of the material.
J. Porous inner core flex duct. Flexible ducts having porous inner cores shall have a non-porous layer or air barrier between the inner core and the outer vapor barrier.
K. Duct system sealing and leakage testing. When space conditioning systems utilize forced air duct systems to supply conditioned air to an individual dwelling unit, the ducts shall be sealed, as confirmed through field verification and diagnostic testing, in accordance with all applicable procedures specified in Reference Residential Appendix RA3.1. Air handler airflow for calculation of duct leakage rate compliance targets shall be determined according to methods specified in Reference Residential Appendix RA3.1.4.2.
For multifamily dwellings with the air-handling unit installed and the ducts connected directly to the air handler, regardless of duct system location:
i. The total leakage of the
duct system shall not exceed 12 percent of the air handler airflow as determined utilizing the procedures in Reference Residential Appendix Section
RA3.1.4.3.1; or
ii. The
duct system leakage to outside shall not exceed 6 percent of the air handler airflow as determined utilizing the procedures in Reference Residential Appendix Section
RA3.1.4.3.4.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(b)5K: The HERS Rater field verification and HERS Provider data registry requirements of Reference Residential Appendix RA2 and RA3 are not required for multifamily dwelling units in buildings four habitable stories and greater. The installer shall certify that diagnostic testing was performed in accordance with the applicable procedures.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(b)5K: Multifamily dwelling units in buildings four habitable stories and greater in Climate Zones 1, 3, 5, and 7.
L. System airflow rate and fan efficacy. Space-conditioning systems that utilize forced air ducts to supply cooling to an individual dwelling unit shall:
i. Static pressure probe. Have a hole for the placement of a static pressure probe (HSPP), or a permanently installed static pressure probe (PSPP) in the supply plenum downstream of the air conditioning evaporator coil. The size, location, and labeling of the HSPP or PSPP shall conform to the requirements specified in Reference Residential Appendix
RA3.3.1.1 as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing; and
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(b)5Li: Systems that cannot conform to the specifications for hole location in Reference Residential Appendix Figure RA3.3-1 shall not be required to provide holes as described in Figure RA3.3-1.
ii. Single zone central forced air systems. Demonstrate, in every control mode, airflow greater than or equal to 350 cfm per ton of nominal cooling capacity through the return grilles, and an air-handling unit fan efficacy less than or equal to the maximum W/cfm specified in subsections a or b below. The airflow rate and fan efficacy requirements in this section shall be confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures given in Reference Residential Appendix
RA3.3.
a. 0.45 W/cfm for gas furnace air-handling units.
b. 0.58 W/cfm for air-handling units that are not gas furnaces.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(b)5Lii: Standard ducted systems without zoning dampers may comply by meeting the applicable requirements in TABLE 160.3-A or 160.3-B as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures in Reference Residential Appendix Sections RA3.1.4.4 and RA3.1.4.5. The design clean-filter pressure drop requirements specified by Section 160.2(b)1Div for the system air filter(s) shall conform to the requirements given in TABLE 160.3-A or 160.3-B.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(b)5Lii: Multispeed compressor systems or variable speed compressor systems shall verify airflow (cfm/ton) and fan efficacy (Watt/cfm) for system operation at the maximum compressor speed and the maximum air handler fan speed.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 160.3(b)5Lii: Gas furnace air-handling units manufactured prior to July 3, 2019 shall comply with a fan efficacy value less than or equal to 0.58 w/cfm as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures given in Reference Residential Appendix RA3.3.
iii. Zonally controlled central forced air systems. Zonally controlled central forced air cooling systems shall be capable of simultaneously delivering, in every zonal control mode, an airflow from the dwelling, through the air handler fan and delivered to the
dwelling, of greater than or equal to 350 CFM per ton of nominal cooling capacity, and operating at an air-handling unit fan efficacy of less than or equal to the maximum W/cfm specified in subsections a or b below. The airflow rate and fan efficacy requirements in this section shall be confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the applicable procedures specified in Reference Residential Appendix
RA3.3.
a. 0.45 W/cfm for gas furnace air-handling units.
b. 0.58 W/cfm for air-handling units that are not gas furnaces.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(b)5Liii: Multispeed or variable speed compressor systems, or single speed compressor systems that utilize the performance compliance approach, shall demonstrate compliance with the airflow (cfm/ton) and fan efficacy (Watt/cfm) requirements of Section 160.3(b)5Liii by operating the system at maximum compressor capacity and system fan speed with all zones calling for conditioning, rather than in every zonal control mode.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(b)5Liii: Gas furnace air-handling units manufactured prior to July 3, 2019 shall comply with a fan efficacy value less than or equal to 0.58 w/cfm as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures given in Reference Residential Appendix RA3.3.
iv. Small duct high velocity forced air systems. Demonstrate, in every control mode, airflow greater than or equal to 250 cfm per ton of nominal cooling capacity through the return grilles, and an air-handling unit fan efficacy less than or equal to 0.62 W/cfm as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures given in Reference Residential Appendix
RA3.3
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(b)5Liv: Standard ducted systems without zoning dampers may comply by meeting the applicable requirements in TABLE 160.3-A or 160.3-B as confirmed by field verification and diagnostic testing in accordance with the procedures in Reference Residential Appendix Sections RA3.1.4.4 and RA3.1.4.5. The design clean-filter pressure drop requirements specified by Section 160.2(b)1Div for the system air filter(s) shall conform to the requirements given in TABLE 160.3-A or 160.3-B.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(b)5Liv: Multispeed compressor systems or variable speed compressor systems shall verify airflow (cfm/ton) and fan efficacy (watt/cfm) for system operation at the maximum compressor speed and the maximum air handler fan speed.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(b)5L: The HERS Rater field verification and HERS Provider data registry requirements of Reference Residential Appendix RA2 and RA3 are not required for multifamily dwelling units in buildings four habitable stories and greater. The installer shall certify that diagnostic testing was performed in accordance with the applicable procedures.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(b)5L: Multifamily dwelling units in buildings four habitable stories and greater in Climate Zone 1.
A. General requirements. The piping conditions listed below for space-conditioning systems with fluid normal operating temperatures
listed in
Table 160.3-D, shall have at least the amount of insulation specified in Section
160.3(c)1D:
i. Space cooling systems. All refrigerant suction, chilled water, and brine fluid distribution systems.
ii. Space heating systems. All refrigerant, steam, steam condensate and hot water fluid distribution systems.
Exception to Section 160.3(c)1Aii: Heat pumps refrigerant vapor line shall be installed with a minimum of 0.75 inch thick or R-6.0 insulation. No insulation is required on the refrigerant liquid line.
B. Insulation conductivity shall be determined in accordance with ASTM C335 at the mean temperature
listed in
Table 160.3-D, and shall be rounded to the nearest 1/100 Btu-inch per hour per square foot per °F. Fluid distribution systems include all elements that are in series with the fluid flow, such as pipes, pumps, valves, strainers, coil u-bends, and air separators, but not including elements that are not in series with the fluid flow, such as expansion tanks, fill lines, chemical feeders, and drains.
C. Insulation protection. Pipe Insulation shall be protected from damage due to sunlight, moisture, equipment maintenance, and wind. Protection shall, at minimum, include the following:
i. Pipe insulation exposed to weather shall be protected by a cover suitable for outdoor service. The cover shall be water retardant and provide shielding from solar radiation that can cause degradation of the material. Adhesive tape shall not be used to provide this protection.
ii. Pipe insulation covering chilled water piping and refrigerant suction piping located outside the conditioned space shall include, or be protected by, a Class I or Class II vapor retarder. All penetrations and joints shall be sealed.
iii. Pipe insulation buried below grade must be installed in a waterproof and non-crushable casing or sleeve.
i. For insulation with a conductivity in the range shown in
Table 160.3-D for the applicable fluid temperature range, the insulation shall have the applicable minimum thickness or R-value shown in Table 160.3-D.
ii. For insulation with a conductivity outside the range shown in
Table 160.3-D for the applicable fluid temperature range, the insulation shall have a minimum
R-value shown in 160.3-D or thickness as calculated with Equation 160.3-A:
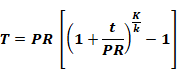
WHERE:
T = Minimum insulation thickness for material with conductivity K, inches.
PR = Pipe actual outside radius, inches.
t = Insulation thickness from Table 160.3-D, inches.
K = Conductivity of alternate material at the mean rating temperature indicated in Table 160.3-D for the applicable fluid temperature range, in Btu-inch per hour per square foot per °F.
k = The lower value of the conductivity range listed in Table 160.3-D for the applicable fluid temperature range, Btu-inch per hour per square foot per °F.
EXCEPTION 1 to Section 160.3(c)1: Factory-installed piping within space-conditioning equipment certified under Section 110.1 or 110.2.
EXCEPTION 2 to Section 160.3(c)1: Piping that conveys fluids with a design operating temperature range between 60°F and 105°F.
EXCEPTION 3 to Section 160.3(c)1: Where the heat gain or heat loss to or from piping without insulation will not increase building source energy use.
EXCEPTION 4 to Section 160.3(c)1: Piping that penetrates framing members shall not be required to have pipe insulation for the distance of the framing penetration. Metal piping that penetrates metal framing shall use grommets, plugs, wrapping or other insulating material to ensure that no contact is made with the metal framing.
2. Requirements for air distribution system, ducts, and plenum. Multifamily common areas shall comply with the applicable requirements of Sections
160.3(c)2A through
160.3(c)2F.
A. CMC compliance. All air distribution system ducts and plenums, including, but not limited to, building cavities, mechanical closets, air-handler boxes and support platforms used as ducts or plenums, shall meet the requirements of CMC Sections 601.0, 602.0, 603.0, 604.0, 605.0, and ANSI/SMACNA-006-2006 HVAC Duct Construction Standards Metal and Flexible 3rd Edition, incorporated herein by reference. Connections of metal ducts and the inner core of flexible ducts shall be mechanically fastened. Openings shall be sealed with mastic, tape, aerosol sealant, or other duct-closure system that meets the applicable requirements of UL 181, UL 181A, or UL 181B. If mastic or tape is used to seal openings greater than 1/4 inch, the combination of mastic and either mesh or tape shall be used.
B. Portions of supply-air and return-air ducts conveying heated or cooled air located in one or more of the following spaces shall be insulated to a minimum installed level of R-8:
ii. In a space between the roof and an insulated ceiling; or
iii. In a space directly under a
roof with fixed vents or openings to the outside or unconditioned spaces; or
iv. In an unconditioned crawlspace; or
v. In other unconditioned spaces.
Portions of supply-air ducts that are not in one of these spaces, including ducts buried in concrete slab, shall be insulated to a minimum installed level of R-4.2 or be enclosed in directly conditioned space.
i. Factory-fabricated duct systems.
a. All
factory-fabricated duct systems shall comply with UL 181 for ducts and closure systems, including collars, connections, and splices, and be labeled as complying with UL 181.
UL 181 testing may be performed by UL laboratories or a laboratory approved by the Executive Director.
b. All pressure-sensitive tapes, heat-activated tapes, and mastics used in the manufacture of rigid fiberglass ducts shall comply with
UL 181 and UL 181A.
c. All pressure-sensitive tapes and mastics used with flexible ducts shall comply with
UL 181 and UL 181B.
d. Ductwork and plenums with pressure class ratings shall be constructed to Seal Class A. Joints and seams of duct systems and their components shall not be sealed with cloth back rubber adhesive duct tapes unless such tape is used in combination with mastic and drawbands.
EXCEPTION to Section 160.3(c)2Cid: Ductwork located in occupied space and exposed to view.
ii. Field-fabricated duct systems.
a.
Factory-made rigid fiberglass and flexible ducts for
field-fabricated duct systems shall comply with
UL 181. All pressure-sensitive tapes, mastics, aerosol sealants, or other closure systems used for installing
field-fabricated duct systems shall meet the applicable requirements of
UL 181, UL 181A, and UL 181B.
b. Mastic sealants and mesh.
I. Sealants shall comply with the applicable requirements of
UL 181, UL 181A, and
UL 181B, and be nontoxic and water resistant.
II. Sealants for interior applications shall pass ASTM C731 (extrudability after aging) and D2202 (slump test on vertical surfaces), incorporated herein by reference.
III. Sealants for exterior applications shall pass ASTM C731, C732 (artificial weathering test), and D2202, incorporated herein by reference.
IV. Sealants and meshes shall be rated for exterior use.
c. Pressure-sensitive tape.Pressure-sensitive tapes shall comply with the applicable requirements of
UL 181, UL 181A, and UL 181B.
d. Ductwork and plenums with pressure class ratings shall be constructed to Seal Class A. Joints and seams of duct systems and their components shall not be sealed with cloth back rubber adhesive duct tapes unless such tape is used in combination with mastic and drawbands.
e. Drawbands used with flexible duct.
I. Drawbands shall be either stainless-steel worm-drive hose clamps or UV-resistant nylon duct ties.
II. Drawbands shall have a minimum tensile strength rating of 150 pounds.
III. Drawbands shall be tightened as recommended by the manufacturer with an adjustable tensioning tool.
f. Aerosol-sealant closures.
I. Aerosol sealants shall meet the requirements of UL 723 and be applied according to manufacturer specifications.
II. Tapes or mastics used in combination with aerosol sealing shall meet the requirements of this section.
D. All duct insulation product R-values shall be based on insulation only (excluding air films, vapor retarders, or other duct components) and tested C-values at 75°F mean temperature at the installed thickness, in accordance with ASTM C518 or ASTM C177, incorporated herein by reference, and certified pursuant to Section
110.8.
i. For duct board, duct liner, and factory-made rigid ducts not normally subjected to compression, the nominal insulation thickness shall be used.
ii. For duct wrap, installed thickness shall be assumed to be 75 percent (25 percent compression) of nominal thickness.
iii. For
factory-made flexible air ducts, the installed thickness shall be determined by dividing the difference between the actual outside diameter and nominal inside diameter by two.
F. Insulated flexible duct products installed to meet this requirement must include labels, in maximum intervals of 3 feet, showing the thermal performance R-value for the duct insulation itself (excluding air films, vapor retarder, or other duct components), based on the tests in Section
160.3(c)2D and the installed thickness determined by Section
160.3(c)2Eiii.
G. Insulation shall be protected from damage, including that due to sunlight, moisture, equipment maintenance, and wind but not limited to the following: Insulation exposed to weather shall be suitable for outdoor service e.g., protected by aluminum, sheet metal, painted canvas, or plastic cover. Cellular foam insulation shall be protected as above or painted with a coating that is water retardant and provides shielding from solar radiation that can cause degradation of the material.
H. Duct systems shall be tested in accordance with i or ii below:
i. New duct systems that meet the criteria in Subsections a, b and c below or ductwork that is part of a system that meets the criteria of Section
180.2(b)2B shall be sealed to a leakage rate not to exceed 6 percent of the nominal air handler airflow rate as confirmed through field verification and diagnostic testing, in accordance with the applicable procedures in
Reference Nonresidential Appendices
NA1 and
NA2.
a. The duct system provides conditioned air to an occupiable space for a constant volume, single zone, space-conditioning system; and
b. The space conditioning system serves less than 5,000 square feet of conditioned floor area; and
c. The combined surface area of the ducts located in the following spaces is more than 25 percent of the total surface area of the entire duct system:
I. Outdoors; or
II. In a space directly under a roof that has a U-factor greater than the U-factor of the ceiling, or if the roof does not meet the requirements of Section 170.2(a)1; or
III. In a space directly under a roof that has fixed vents or openings to the outside or unconditioned spaces; or
IV. In an unconditioned crawlspace; or
V. In other unconditioned spaces.
ii. All duct systems that do not meet the criteria in Section
160.3(c)2H shall meet the duct leakage testing requirements of CMC Section 603.9.2.
B. Constant volume, single zone air conditioning and heat pump unit controls shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.2.
C. Duct systems shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.3 where either:
a. They are new duct systems; or
b. They are part of an altered system.
E. Demand control ventilation systems required by Section 160.2(c)3 shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.5.
J. Automatic demand shed controls shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.10.
K. Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD) for Packaged Direct-Expansion Units shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.11.
L.
Automatic Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD) for air handling units and zone terminal units shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.12.
M. Distributed Energy Storage DX AC Systems shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.13.
N. Thermal Energy Storage (TES) Systems shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.14.
O. Supply air temperature reset controls shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.5.15.
Q. When an Energy Management Control System is installed, it shall functionally meet all of the applicable requirements of Part 6.
A. In multifamily buildings with four or more habitable stories, dwelling unit ventilation systems shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.18.1.
B. In multifamily buildings with four or more habitable stories,
dwelling unit enclosure leakage shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.18.2 when exhaust or supply ventilation systems are used for compliance with whole-
dwelling unit ventilation requirements as specified in Section
160.2(b)2Aivb2.
C. Multifamily building central ventilation ducts in multifamily buildings with four or more habitable stories shall be leak tested in accordance with
NA7.18.3.
D. Multifamily building central ventilation system heat recovery or energy recovery systems in multifamily buildings with four or more habitable stories shall be tested in accordance with
NA7.18.4.
TABLE 160.3-A: Return Duct Sizing for Single Return Duct Systems
Return duct length shall not exceed 30 feet and shall contain no more than 180 degrees of bend. If the total bending exceeds 90 degrees, one bend shall be a metal elbow. Return grille devices shall be labeled in accordance with the requirements in Section 160.2(b)1Biv to disclose the grille's design airflow rate and a maximum allowable clean-filter pressure drop of 25 Pa (0.1 inches water) for the air filter when tested using ASHRAE Standard 52.2, or as rated in accordance with AHRI Standard 680 for the design airflow rate for the return grille. |
System Nominal Cooling Capacity (Ton) * | Return Duct Minimum Nominal Diameter (inch) | Minimum Total Return Filter Grille Nominal Area(inch 2 ) |
| | |
| | |
| | |
* Not applicable to systems with nominal cooling capacity greater than 2.5 tons or less than 1.5 ton. |
TABLE 160.3-B: Return Duct Sizing for Multiple Return Duct Systems
Each return duct length shall not exceed 30 feet and shall contain no more than 180 degrees of bend. If the total bending exceeds 90 degrees, one bend shall be a metal elbow. Return grille devices shall be labeled in accordance with the requirements in Section 160.2(b)1Biv to disclose the grille's design airflow rate and a maximum allowable clean-filter pressure drop of 25 Pa (0.1 inches water) for the air filter when tested using ASHRAE Standard 52.2, or as rated in accordance with AHRI Standard 680 for the design airflow rate for the return grille. |
System Nominal Cooling Capacity (Ton)* | Return Duct 1 Minimum Nominal Diameter (inch) | Return Duct 2 Minimum Nominal Diameter (inch) | Minimum Total Return Filter Grille Nominal Area (inch2 ) |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
* Not applicable to systems with nominal cooling capacity greater than 5.0 tons or less than 1.5 tons. |
TABLE 160.3-C DDC Applications and Qualifications
| | |
Newly Constructed Buildings | Air handling system and all zones served by the system | Individual systems supplying more than three zones and with design heating or cooling capacity of 300 kBtu /h and larger |
Newly Constructed Buildings | Chilled water plant and all coils and terminal units served by the system | Individual plants supplying more than three zones and with design cooling capacity of 300 kBtu /h (87.9 kW) and larger |
Newly Constructed Buildings | Hot water plant and all coils and terminal units served by the system | Individual plants supplying more than three zones and with design heating capacity of 300 kBtu /h (87.9 kW) and larger |
| Zone terminal unit such as VAV box | Where existing zones served by the same air handling, chilled water, or hot water systems that have DDC |
| Air handling system or fan coil | Where existing air handling system(s) and fan coil(s) served by the same chilled or hot water plant have DDC |
| New air handling system and all new zones served by the system | Individual systems with design heating or cooling capacity of 300 kBtu /h and larger and supplying more than three zones and more than 75 percent of zones are new |
| New or upgraded chilled water plant | Where all chillers are new and plant design cooling capacity is 300 kBtu /h (87.9 kW) and larger |
| New or upgraded hot water plant | Where all boilers are new and plant design heating capacity is 300 kBtu /h (87.9 kW) and larger |
TABLE 160.3-D PIPE INSULATION THICKNESS
Fluid Operating Temperature Range (°F) | | | Nominal Pipe Diameter (in inches) |
Conductivity
(in
Btu·in /h·ft2 ·°F) | Mean Rating Temperature (°F) | |
| | | | | | |
Space heating (Steam, Steam Condensate, Refrigerant, Space Heating) | Minimum Pipe Insulation Required (Thickness in inches or R-value) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
Fluid Operating Temperature Range (°F) | | | Nominal Pipe Diameter (in inches) |
Conductivity
(in
Btu·in /h·ft2 ·°F) | Mean Rating Temperature (°F) | | | | | | |
Space cooling systems (chilled water, refrigerant and brine) | Minimum Pipe Insulation Required (Thickness in inches or R-value)1 |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
Footnote to TABLE 160.3-D:
1. These thicknesses are based on energy efficiency considerations only. Issues such as water vapor permeability or surface condensation sometimes require vapor retarders or additional insulation. |
NOTE: Authority: Sections 25213, 25218, 25218.5, 25402 and 25402.1, Public Resources Code. Reference: Sections 25007, 25008, 25218.5, 25310, 25402, 25402.1, 25402.4, 25402.5, 25402.8, and 25943, Public Resources Code.